Complex formation between the postsynaptic scaffolding protein gephyrin, profilin, and Mena: a possible link to the microfilament system
- PMID: 12967995
- PMCID: PMC6740687
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-23-08330.2003
Complex formation between the postsynaptic scaffolding protein gephyrin, profilin, and Mena: a possible link to the microfilament system
Abstract
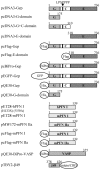
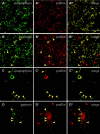
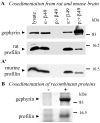
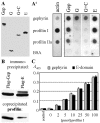
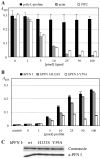
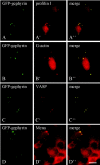
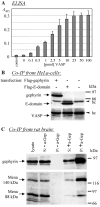
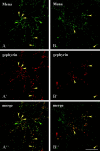
Gephyrin is an essential component of the postsynaptic cortical protein network of inhibitory synapses. Gephyrin-based scaffolds participate in the assembly as well as the dynamics of receptor clusters by connecting the cytoplasmic domains of glycine and GABA(A) receptor polypeptides to two cytoskeletal systems, microtubules and microfilaments. Although there is evidence for a physical linkage between gephyrin and microtubules, the interaction between gephyrin and microfilaments is not well understood so far. Here, we show that neuronal gephyrin interacts directly with key regulators of microfilament dynamics, profilin I and neuronal profilin IIa, and with microfilament adaptors of the mammalian enabled (Mena)/vasodilator stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) family, including neuronal Mena. Profilin and Mena/VASP coprecipitate with gephyrin from tissue and cells, and complex formation requires the E-domain of gephyrin, not the proline-rich central domain. Consequently, gephyrin is not a ligand for the proline-binding motif of profilins, as suspected previously. Instead, it competes with G-actin and phospholipids for the same binding site on profilin. Gephyrin, profilin, and Mena/VASP colocalize at synapses of rat spinal cord and cultivated neurons and in gephyrin clusters expressed in transfected cells. Thus, Mena/VASP and profilin can contribute to the postulated linkage between receptors, gephyrin scaffolds, and the microfilament system and may regulate the microfilament-dependent receptor packing density and dynamics at inhibitory synapses.
Figures

References
-
- Bear JE, Svitkina TM, Krause M, Schafer DA, Loureiro JJ, Strasser GA, Maly IV, Chaga OY, Cooper JA, Borisy GG, Gertler FB ( 2002) Antagonism between Ena/VASP proteins and actin filament capping regulates fibroblast motility. Cell 109 : 509-521. - PubMed
-
- Bjorkegren C, Rozycki M, Schutt CE, Lindberg U, Karlsson R ( 1993) Mutagenesis of human profilin locates its poly(l-proline)-binding site to a hydrophobic patch of aromatic amino acids. FEBS Lett 333 : 123-126. - PubMed
-
- Carlsson L, Nystrom L, Sundkvist I, Markey F, Lindberg U ( 1976) Profilin, a low-molecular weight protein controlling actin polymerisability. In: Contractile systems in non-muscle tissues (Perry SV, Margreth A, Adelstein RS, eds), pp 39-49. Amsterdam: North Holland.
-
- Cramer LP ( 2002) Ena/Vasp: solving a cell motility paradox. Curr Biol 12 : R417-R419. - PubMed
-
- Di Nardo A, Gareus R, Kwiatkowski D, Witke W ( 2000) Alternative splicing of the mouse profilin II gene generates functionally different profilin isoforms. J Cell Sci 113 : 3795-3803. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
