Protein kinase C-mediated Ca2+ entry in HEK 293 cells transiently expressing human TRPV4
- PMID: 12970074
- PMCID: PMC1574039
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705443
Protein kinase C-mediated Ca2+ entry in HEK 293 cells transiently expressing human TRPV4
Abstract
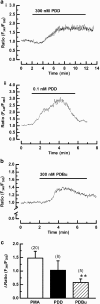
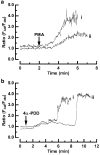
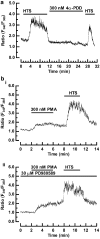
1. We investigated whether protein kinase C (PKC) activation stimulates Ca2+ entry in HEK 293 cells transfected with human TRPV4 cDNA and loaded with fura-2. 2. Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), a PKC-activating phorbol ester, increased the intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) in a dose-dependent manner, with an EC50 value of 11.7 nm. Exposure to a hypotonic solution (HTS) after PMA further increased [Ca2+]i. Two other PKC-activating phorbol esters, phorbol 12,13-didecanoate (PDD) and phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate, also caused [Ca2+]i to increase. 3. The inactive isomer 4alpha-PMA was less effective and the peak [Ca2+]i increase was significantly smaller than that induced by PMA. In contrast, 4alpha-PDD produced a monophasic or biphasic [Ca2+]i increase with a different latency, while 4alpha-phorbol had no effect. 4. The PMA-induced [Ca2+]i increase was abolished by prior exposure to bisindolylmaleimide (BIM), a PKC-specific inhibitor, and suppressed by the nonspecific PKC inhibitor 1-(5-isoquinolinesulphonyl)-2-methylpiperazine. The [Ca2+]i increase induced by 4alpha-PMA, 4alpha-PDD or HTS was not significantly affected by BIM. 5. These results suggest that both PKC-dependent and -independent mechanisms are involved in the phorbol ester-induced activation of TRPV4, and the PKC-independent pathway is predominant in HTS-induced Ca2+ entry.
Figures




References
-
- BRAKEMEIER S., EICHLER I., HOPP H., KOHLER R., HOYER J. Up-regulation of endothelial stretch-activated cation channels by fluid shear stress. Cardiovasc. Res. 2002;53:209–218. - PubMed
-
- CHEN Y., SIMASKO S.M., NIGGEL J., SIGURDSON W.J., SACHS F. Ca2+ uptake in GH3 cells during hypotonic swelling: the sensory role of stretch-activated ion channels. Am. J. Physiol. 1996;270:C1790–C1798. - PubMed
-
- CHENG J.-J., WUNG B.-S., CHAO Y.-J., WANG D.L. Sequential activation of protein kinase C (PKC)-α and PKC-ɛ contributes to sustained Raf/ERK1/2 activation in endothelial cells under mechanical strain. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:31368–31375. - PubMed
-
- DELANY N.S., HURLE M., FACER P., ALNADAF T., PLUMPTON C., KINGHORN I., SEE C.G., COSTIGAN M., ANAND P., WOOLF C.J., CROWTHER D., SANSEAU P., TATE S.N. Identification and characterization of a novel human vanilloid receptor-like protein, VRL-2. Physiol. Genomics. 2001;4:165–174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

