Effects of the CGRP receptor antagonist BIBN4096BS on capsaicin-induced carotid haemodynamic changes in anaesthetised pigs
- PMID: 12970078
- PMCID: PMC1574043
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705451
Effects of the CGRP receptor antagonist BIBN4096BS on capsaicin-induced carotid haemodynamic changes in anaesthetised pigs
Abstract
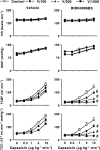
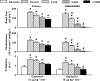
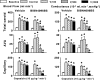
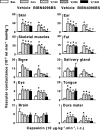
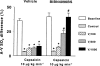
1. Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), a potent vasodilator released from capsaicin-sensitive trigeminal sensory nerves, seems to be involved in the pathogenesis of migraine. Hence, CGRP receptor antagonists may serve as a novel treatment for migraine. This study was therefore designed to investigate the effects of BIBN4096BS (100, 300 and 1000 microg kg-1, i.v.), a potent and selective CGRP receptor antagonist, on capsaicin-induced carotid haemodynamic changes in anaesthetised pigs. Both vagosympathetic trunks were cut and phenylephrine was infused into the carotid artery (i.c.) to support carotid vascular tone. 2. Infusions of capsaicin (0.3, 1, 3 and 10 microg kg-1 min-1, i.c.) did not alter the heart rate, but dose-dependently increased the mean arterial blood pressure. This moderate hypertensive effect was not modified by BIBN4096BS. 3. Capsaicin infusion (10 microg kg-1 min-1, i.c.) increased total carotid, arteriovenous anastomotic and tissue blood flows and conductances as well as carotid pulsations, but decreased the difference between arterial and jugular venous oxygen saturations. These responses to capsaicin were dose-dependently blocked by BIBN4096BS. 4. Capsaicin infusion (10 microg kg-1 min-1, i.c.) more than doubled the jugular venous plasma concentration of CGRP. This effect was not blocked, but rather increased, by BIBN4096BS. 5. The above results show that BIBN4096BS behaves as a potent antagonist of capsaicin-induced carotid haemodynamic changes that are mediated via the release of CGRP. Therefore, this compound may prove effective in the treatment of migraine.
Figures
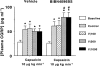
Similar articles
-
Lack of effect of the adenosine A1 receptor agonist, GR79236, on capsaicin-induced CGRP release in anaesthetized pigs.Cephalalgia. 2005 Nov;25(11):1082-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-2982.2005.00967.x. Cephalalgia. 2005. PMID: 16232161
-
Effects of sumatriptan on capsaicin-induced carotid haemodynamic changes and CGRP release in anaesthetized pigs.Cephalalgia. 2004 Sep;24(9):717-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-2982.2004.00743.x. Cephalalgia. 2004. PMID: 15315527
-
Clonidine inhibits the canine external carotid vasodilatation to capsaicin by alpha2A/2C-adrenoceptors.Eur J Pharmacol. 2006 Aug 14;543(1-3):68-76. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.05.041. Epub 2006 Jun 2. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16814767
-
Development and potential of non-peptide antagonists for calcitonin-gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptors: evidence for CGRP receptor heterogeneity.Biochem Soc Trans. 2002 Aug;30(4):468-73. doi: 10.1042/bst0300468. Biochem Soc Trans. 2002. PMID: 12196117 Review.
-
Migraine and beyond: cardiovascular therapeutic potential for CGRP modulators.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2001 Jun;10(6):1131-8. doi: 10.1517/13543784.10.6.1131. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2001. PMID: 11772240 Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of calcitonin gene-related peptide in the skin, and other physiological and pathophysiological functions.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2021 Oct 5;18:100361. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2021.100361. eCollection 2021 Dec. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2021. PMID: 34746878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Donitriptan, but not sumatriptan, inhibits capsaicin-induced canine external carotid vasodilatation via 5-HT1B rather than 5-HT1D receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Sep;149(1):82-91. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706839. Epub 2006 Jul 31. Br J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16880765 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical mediators of migraine: preclinical and clinical observations.Headache. 2011 Jun;51(6):1029-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2011.01929.x. Headache. 2011. PMID: 21631491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current and prospective pharmacological targets in relation to antimigraine action.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2008 Oct;378(4):371-94. doi: 10.1007/s00210-008-0322-7. Epub 2008 Jul 15. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18626630 Review.
-
Haemodynamic profile and responsiveness to anandamide of TRPV1 receptor knock-out mice.J Physiol. 2004 Jul 15;558(Pt 2):647-57. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.064824. Epub 2004 Apr 30. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15121805 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ALVING K., MATRAN R., LUNDBERG J.M. Capsaicin-induced local effector responses, autonomic reflexes and sensory neuropeptide depletion in the pig. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 1991;343:37–45. - PubMed
-
- ARDEN W.A., FISCUS R.R., WANG X., YANG L., MALEY R., NIELSEN M., LANZO S., GROSS D.R. Elevations in circulating calcitonin gene-related peptide correlate with hemodynamic deterioration during endotoxic shock in pigs. Circ. Shock. 1994;42:147–153. - PubMed
-
- ASHINA M., BENDTSEN L., JENSEN R., SCHIFTER S., OLESEN J. Evidence for increased plasma levels of calcitonin gene-related peptide in migraine outside of attacks. Pain. 2000;86:133–138. - PubMed
-
- BELL D., MCDERMOTT B.J. Calcitonin gene-related peptide in the cardiovascular system: characterization of receptor populations and their (patho)physiological significance. Pharmacol. Rev. 1996;48:253–288. - PubMed
-
- BRAIN S.D., WILLIAMS T.J., TIPPINS J.R., MORRIS H.R., MACINTYRE I. Calcitonin gene-related peptide is a potent vasodilator. Nature. 1985;313:54–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

