The ability of neuropeptide Y to mediate responses in the murine cutaneous microvasculature: an analysis of the contribution of Y1 and Y2 receptors
- PMID: 12970079
- PMCID: PMC1574044
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705452
The ability of neuropeptide Y to mediate responses in the murine cutaneous microvasculature: an analysis of the contribution of Y1 and Y2 receptors
Abstract
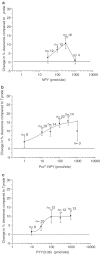
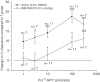
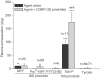
1. The ability of neuropeptide Y (NPY) to modulate skin blood flow, oedema formation and neutrophil accumulation was investigated. Experiments were designed to examine the possible contribution of the Y2 receptor, in addition to the Y1 receptor, through use of Y2 receptor knockout mice (Y2-/-) and selective receptor antagonists. 2. The development of a 99mTc clearance technique for the measurement of microvascular blood flow changes in mouse dorsal skin revealed a dose-dependent ability of picomole amounts of NPY, and also of the Y1-preferred agonist Pro34NPY and the Y2-preferred agonist PYY(3-36) to decrease blood flow. 3. The Y1 receptor antagonist BIBO3304 blocked responses to the Y1 agonist at the lower doses, but only partially inhibited at the higher doses tested in Y2+/+. In Y2-/- receptor mice, the responses to the Y2 agonist were abolished at the lower doses and partially reduced at the highest dose tested, while those to the Y1 agonist were similar in both Y2+/+ and Y2-/-receptor mice. 4. In Y2+/+ receptor mice, the simultaneous injection of the Y2 antagonist BIIE0246 with BIBO3304 abolished Y2 agonist-induced decreases in blood flow over the dose range used (10-100 pmol). When the Y2 receptor antagonist BIIE0246 was given alone, it was not able to significantly affect the PYY(3-36)-induced response, whereas the Y1 receptor antagonist BIBO3304 partially (P<0.001) inhibited the decrease in blood flow evoked by PYY(3-36) at the highest dose. 5. NPY did not mediate either oedema formation, even when investigated in the presence of the vasodilator calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), or neutrophil accumulation in murine skin. 6. We conclude that the major vasoactive activity of NPY in the cutaneous microvasculature is to act in a potent manner to decrease blood flow via Y1 receptors, with evidence for the additional involvement of postjunctional Y2 receptors. Our results do not provide evidence for a potent proinflammatory activity of NPY in the cutaneous microvasculature.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Functional consequences of neuropeptide Y Y 2 receptor knockout and Y2 antagonism in mouse and human colonic tissues.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Jun;139(4):863-71. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705298. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12813010 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropeptide Y, Y1, Y2 and Y4 receptors mediate Y agonist responses in isolated human colon mucosa.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Mar;135(6):1505-12. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704604. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11906964 Free PMC article.
-
Irreversible binding kinetics of neuropeptide Y ligands to Y2 but not to Y1 and Y5 receptors.Pharmacology. 2005 Dec;75(1):21-9. doi: 10.1159/000085897. Epub 2005 May 20. Pharmacology. 2005. PMID: 15908753
-
Neuropeptide Y Y1 receptor mechanisms in sympathetic vascular control.Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1997;636:1-55. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1997. PMID: 9179320 Review.
-
Neuropeptide Y receptor subtypes, Y1 and Y2.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;611:7-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb48918.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990. PMID: 2174225 Review.
Cited by
-
Topical Neuropeptide Y for Ischemic Skin Wounds.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 15;25(6):3346. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063346. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542321 Free PMC article.
-
Alarin is a vasoactive peptide.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jun 12;104(24):10217-22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0608585104. Epub 2007 May 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17535903 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropeptide Y2 receptors are involved in enhanced neurogenic vasoconstriction in spontaneously hypertensive rats.Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Jul;148(5):703-13. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706774. Epub 2006 May 22. Br J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16715120 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropeptide Y and neurovascular control in skeletal muscle and skin.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2009 Sep;297(3):R546-55. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00157.2009. Epub 2009 Jul 1. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19571208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Insights Into the Role of Neuropeptide Y in Skin Physiology and Pathology.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 28;13:838434. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.838434. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35418942 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- BATTERHAM R.L., COWLEY M.A., SMALL C.J., HERZOG H., COHEN M.A., DAKIN C.L., WREN A.M., BRYNES A.E., LOW M.J., GHATEI M.A., CONE R.D., BLOOM S.R. Gut hormone PYY(3–36) physiologically inhibits food intake. Nature. 2002;418:650–654. - PubMed
-
- BÖTTCHER G., SJÖLUND K., EKBLAD E., HÅKANSON R., SCHWARTZ T.W., SUNDLER F. Coexistence of peptide YY and glicentin immunoreactivity in endocrine cells of the gut. Regul. Pept. 1984;8:261–266. - PubMed
-
- CAO T., GERARD N.P., BRAIN S.D. Use of NK(1) knockout mice to analyze substance P-induced edema formation. Am. J. Physiol. 1999;277:R476–R481. - PubMed
-
- CAO T., PINTER E., AL-RASHED S., GERARD N., HOULT J.R., BRAIN S.D. Neurokinin-1 receptor agonists are involved in mediating neutrophil accumulation in the inflamed, but not normal, cutaneous microvasculature: an in vivo study using neurokinin-1 receptor knockout mice. J. Immunol. 2000;164:5424–5429. - PubMed
-
- CHU D.Q., LEGON S., SMITH D.M., COSTA S.K., CUTTITTA F., BRAIN S.D. The calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) antagonist CGRP(8-37) blocks vasodilatation in inflamed rat skin: involvement of adrenomedullin in addition to CGRP. Neurosci. Lett. 2001;310:169–172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

