A model for receptor-peptide binding at the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor through the analysis of truncated ligands and receptors
- PMID: 12970080
- PMCID: PMC1574045
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705453
A model for receptor-peptide binding at the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor through the analysis of truncated ligands and receptors
Abstract
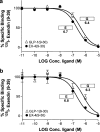
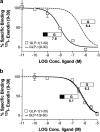
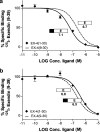
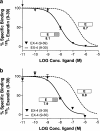
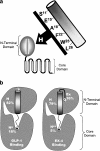
1. The receptor for glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) can be activated by both its physiological hormone and a peptide discovered in the venom of the Gila Monster, exendin-4, which shows promise as an antidiabetic agent. 2. Exendin-4 displays receptor-binding properties not observed for GLP-1. Firstly, exendin-4 can be truncated by up to eight residues at its N-terminus without a significant loss of affinity. Secondly, exendin-4 maintains high affinity for the isolated N-terminal domain of the receptor, suggesting that exendin-4 makes additional contacts with this domain of the receptor, which nullify the requirement for ligand-receptor interactions involving the extracellular loops and/or transmembrane helices of the receptor's core domain. 3. In order to further understand the nature of the receptor-peptide interaction, a variety of full length and truncated peptide analogues were used to quantify the contribution of each distinct region of exendin-4 and GLP-1 to receptor affinity. 4. Our data show that, for both exendin-4 and GLP-1, the primary interaction is between the putative helical region of the peptide and the extracellular N-terminal domain of the receptor. 5. However, we demonstrate that the contribution to receptor affinity provided by the N-terminal segment of GLP-1 is greater than that of exendin-4, while the C-terminal nine residue extension of exendin-4, absent in GLP-1, forms a compensatory interaction with the N-terminal domain of the receptor. 6. We describe a peptide-receptor binding model to account for these data.
Figures
References
-
- BERGWITZ C., GARDELLA T.J., FLANNERY M.R., POTTS J.T., KRONENBERG H.M., GOLDRING S.R., JÜPPNER H. Full activation of chimeric receptors by hybrids between parathyroid hormone and calcitonin. Evidence for a common pattern of ligand–receptor interaction. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:26469–26472. - PubMed
-
- DAKIN C.L., GUNN I., SMALL C.J., EDWARDS C.M.B., HAY D.L., SMITH D.M., GHATEI M.A., BLOOM S.R. Oxyntomodulin inhibits food intake in the rat. Endocrinology. 2001;142:4244–4250. - PubMed
-
- GÖKE R., FEHMANN H.C., LINN T., SCHMIDT H., KRAUSE M., ENG J., GÖKE B. Exendin-4 is a high potency agonist and truncated exendin-(9–39)-amide an antagonist at the glucagon-like peptide-1(7–36)-amide receptor on insulin secreting cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1993;268:19650–19655. - PubMed
-
- GUTNIAK M., ØRSKOV C., HOLST J.J., AHRÉN B., EFFENDIC S. Antidiabetogenic effect of glucagon-like peptide-1(7–36)amide in normal subjects and patients with diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992;326:1316–1322. - PubMed
-
- HJORTH S.A., ADELHORST K., PEDERSEN B.B., KIRK O., SCHWARTZ T.W. Glucagon and glucagon-like peptide 1: selective receptor recognition via distinct peptide epitopes. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:30121–30124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

