Ragaglitazar: a novel PPAR alpha PPAR gamma agonist with potent lipid-lowering and insulin-sensitizing efficacy in animal models
- PMID: 12970088
- PMCID: PMC1574054
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705463
Ragaglitazar: a novel PPAR alpha PPAR gamma agonist with potent lipid-lowering and insulin-sensitizing efficacy in animal models
Abstract
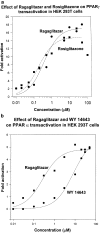
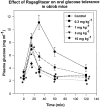
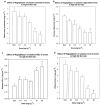
Ragaglitazar [(-) DRF 2725; NNC 61-0029] is a coligand of PPARalpha and PPARgamma. In ob/ob mice, ragaglitazar showed significant reduction in plasma glucose, triglyceride and insulin (ED50 values <0.03, 6.1 and <0.1 mg kg-1). These effects are three-fold better than rosiglitazone and KRP-297. In Zucker fa/fa rats, ragaglitazar showed dose-dependent reduction in triglyceride and insulin, hepatic triglyceride secretion and triglyceride clearance kinetics (maximum of 74, 53, 32 and 50% at 3 mg kg-1), which are better than rosiglitazone and KRP-297. In a high-fat-fed hyperlipidaemic rat model, the compound showed an ED50 of 3.95, 3.78 mg kg-1 for triglyceride and cholesterol lowering, and 0.29 mg kg-1 for HDL-C increase. It also showed improvement in clearance of plasma triglyceride and hepatic triglyceride secretion rate. All these effects are 3-10-fold better than fenofibrate and KRP-297. Ragaglitazar treatment showed significant reduction in plasma Apo B and Apo CIII levels, and increase in liver CPT1 and CAT activity and ACO mRNA. Significant increase of both liver and fat LPL activity and fat aP2 mRNA was also observed. In a high-fat-fed hamster model, ragaglitazar at 1 mg kg-1 showed 83 and 61% reduction in triglyceride and total cholesterol, and also 17% reduction in fat feed-induced body weight increase. In these hyperlipidaemic animal models, PPARgamma ligands failed to show any significant efficacy. Taken together, ragaglitazar shows better insulin-sensitizing and lipid-lowering potential, as compared to the standard compounds.
Figures



References
-
- ARONOFF S., ROSENBALT S., BRAITHWAITE S., EGAN J.W., MATHISEN A.L., SCHNEIDER R.L. Pioglitazone hydrochloride monotherapy improves glycemic control in the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2000;23:1605–1611. - PubMed
-
- ASSIMACOPOULAS-JANNET F., JEANRENAUD B. The hormonal and metabolic basis of experimental obesity. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1976;5:337–365. - PubMed
-
- BALFOUR J.A.B., PLOSKER G.L. Rosiglitazone. Drugs. 1999;57:921–930. - PubMed
-
- BIEBER L.L., ABRAHAM T., HELMRATH T. A rapid spectrophotometric method for carnitine palmitoyltransferase. Anal. Biochem. 1972;50:509–518. - PubMed
-
- BIEBER L.L., MARKWELL M.A.K. Peroxisomal and microsomal carnitine acetyltransferase. Methods Enzymol. 1981;71:351–358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

