CL/RAMP2 and CL/RAMP3 produce pharmacologically distinct adrenomedullin receptors: a comparison of effects of adrenomedullin22-52, CGRP8-37 and BIBN4096BS
- PMID: 12970090
- PMCID: PMC1574059
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705472
CL/RAMP2 and CL/RAMP3 produce pharmacologically distinct adrenomedullin receptors: a comparison of effects of adrenomedullin22-52, CGRP8-37 and BIBN4096BS
Abstract
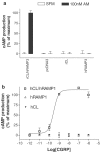
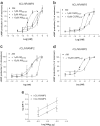
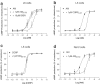
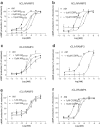
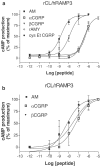
Adrenomedullin (AM) has two known receptors formed by the calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CL) and receptor activity-modifying protein (RAMP) 2 or 3: we report the effects of the antagonist fragments of human AM and CGRP (AM22-52 and CGRP8-37) in inhibiting AM at human (h), rat (r) and mixed species CL/RAMP2 and CL/RAMP3 receptors transiently expressed in Cos 7 cells or endogenously expressed as rCL/rRAMP2 complexes by Rat 2 and L6 cells. AM22-52 (10 microM) antagonised AM at all CL/RAMP2 complexes (apparent pA2 values: 7.34+/-0.14 (hCL/hRAMP2), 7.28+/-0.06 (Rat 2), 7.00+/-0.05 (L6), 6.25+/-0.17 (rCL/hRAMP2)). CGRP8-37 (10 microM) resembled AM22-52 except on the rCL/hRAMP2 complex, where it did not antagonise AM (apparent pA2 values: 7.04+/-0.13 (hCL/hRAMP2), 6.72+/-0.06 (Rat2), 7.03+/-0.12 (L6)). On CL/RAMP3 receptors, 10 microM CGRP8-37 was an effective antagonist at all combinations (apparent pA2 values: 6.96+/-0.08 (hCL/hRAMP3), 6.18+/-0.18 (rCL/rRAMP3), 6.48+/-0.20 (rCL/hRAMP3)). However, 10 microM AM22-52 only antagonised AM at the hCL/hRAMP3 receptor (apparent pA2 6.73+/-0.14). BIBN4096BS (10 microM) did not antagonise AM at any of the receptors. Where investigated (all-rat and rat/human combinations), the agonist potency order on the CL/RAMP3 receptor was AM approximately betaCGRP>alphaCGRP. rRAMP3 showed three apparent polymorphisms, none of which altered its coding sequence. This study shows that on CL/RAMP complexes, AM22-52 has significant selectivity for the CL/RAMP2 combination over the CL/RAMP3 combination. On the mixed species receptor, CGRP8-37 showed the opposite selectivity. Thus, depending on the species, it is possible to discriminate pharmacologically between CL/RAMP2 and CL/RAMP3 AM receptors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The pharmacology of adrenomedullin receptors and their relationship to CGRP receptors.J Mol Neurosci. 2004;22(1-2):105-13. doi: 10.1385/JMN:22:1-2:105. J Mol Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 14742915 Review.
-
Identification of N-terminal receptor activity-modifying protein residues important for calcitonin gene-related peptide, adrenomedullin, and amylin receptor function.Mol Pharmacol. 2008 Oct;74(4):1059-71. doi: 10.1124/mol.108.047142. Epub 2008 Jul 1. Mol Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18593822
-
The seven amino acids of human RAMP2 (86) and RAMP3 (59) are critical for agonist binding to human adrenomedullin receptors.J Biol Chem. 2001 Dec 28;276(52):49459-65. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M108369200. Epub 2001 Oct 8. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11591721
-
Sequencing of a calcitonin receptor-like receptor in salmon Oncorhynchus gorbuscha. Functional studies using the human receptor activity-modifying proteins.Gene. 2002 Oct 2;298(2):203-10. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(02)00974-5. Gene. 2002. PMID: 12426108
-
Adrenomedullin selectivity of calcitonin-like receptor/receptor activity modifying proteins.Hypertens Res. 2003 Feb;26 Suppl:S3-8. doi: 10.1291/hypres.26.s3. Hypertens Res. 2003. PMID: 12630805 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypertension and dysregulated proinflammatory cytokine production in receptor activity-modifying protein 1-deficient mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Oct 16;104(42):16702-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0705974104. Epub 2007 Oct 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17923674 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharide induces calcitonin gene-related peptide in the RAW264.7 macrophage cell line.Immunology. 2010 Jul;130(3):399-409. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03239.x. Epub 2010 Feb 5. Immunology. 2010. PMID: 20141542 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological characterisation of mouse calcitonin and calcitonin receptor-like receptors reveals differences compared with human receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2022 Feb;179(3):416-434. doi: 10.1111/bph.15628. Epub 2021 Oct 15. Br J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34289083 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Adrenomedullin in Oncology: A Feasible Strategy With Potential as Much More Than an Alternative Anti-Angiogenic Therapy.Front Oncol. 2021 Jan 6;10:589218. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.589218. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33489885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting a family B GPCR/RAMP receptor complex: CGRP receptor antagonists and migraine.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 May;166(1):66-78. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01633.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21871019 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- AIYAR N., DISA J., AO Z., XU D., SURYA A., PILLARISETTI K., PARAMESWARAN N., GUPTA S.K., DOUGLAS S.A., NAMBI P. Molecular cloning and pharmacological characterization of bovine calcitonin receptor-like receptor from bovine aortic endothelial cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002;63:1949–1959. - PubMed
-
- AIYAR N., DISA J., PULLEN M., NAMBI P. Receptor activity modifying proteins interaction with human and porcine calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CRLR) in HEK-293 cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2001;224:123–133. - PubMed
-
- AIYAR N., RAND K., ELSHOURBAGY N.A., ZENG Z.Z., ADAMOU J.E., BERGSMA D.J., LI Y. A cDNA encoding the calcitonin-gene-related peptide type-1 receptor J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:11325–11329. - PubMed
-
- ALDECOA A., GUJER R., FISCHER J., BORN W. Mammalian calcitonin receptor-like receptor/receptor modifying protein complexes define calcitonin gene-related peptide and adrenomedullin receptors in Drosophila Schneider 2 cells. FEBS Lett. 2000;471:156–160. - PubMed
-
- BUHLMANN N., LEUTHAUSER K., MUFF R., FISCHER J.A., BORN W. A receptor activity modifying protein (RAMP)2-dependent adrenomedullin receptor is a calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor when coexpressed with human RAMP1. Endocrinology. 1999;140:2883–2890. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

