A single ring of charged amino acids at one end of the pore can control ion selectivity in the 5-HT3 receptor
- PMID: 12970096
- PMCID: PMC1574024
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705424
A single ring of charged amino acids at one end of the pore can control ion selectivity in the 5-HT3 receptor
Abstract
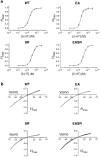
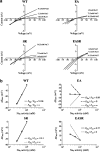
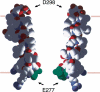
1. To determine the mechanisms by which cation- or anion-specific channels select between these ions, we have examined the role of electrostatic factors in a typical ligand-gated ion channel, the 5-hydroxytryptamine3 (5-HT3) receptor, by removal and/or insertion of rings of conserved charged residues at either end of the pore. 2. Neutralization of the negatively charged ring at the intracellular end of the channel (E-1'A) results in a nonselective channel (PNa/PCl=0.89). 3. Insertion of positively charged residues at the extracellular end of the pore either results in a nonfunctional receptor (A24'K) or one that remains cation-selective (PNa/PCl=110; S19'R). 4. Combining the removal of a negatively charged ring (E-1'A) with the insertion of a positively charged ring (S19'R), however, results in a channel that is predominantly anion-selective (PNa/PCl=0.37). 5. The data suggest that for the cation-selective 5-HT3 receptor, the control of selectivity exerted by charged rings at either end of the pore is dominated by the ring of negatively charged residues at the intracellular side of the channel. As changing the charge at this position has also been shown to change ionic selectivity in anion-selective receptors, these data suggest that electrostatic factors can control selectivity in the whole Cys-loop family.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Modular design of Cys-loop ligand-gated ion channels: functional 5-HT3 and GABA rho1 receptors lacking the large cytoplasmic M3M4 loop.J Gen Physiol. 2008 Feb;131(2):137-46. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200709896. J Gen Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18227272 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosine residues that control binding and gating in the 5-hydroxytryptamine3 receptor revealed by unnatural amino acid mutagenesis.J Neurosci. 2004 Oct 13;24(41):9097-104. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2429-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15483128 Free PMC article.
-
Conversion of the ion selectivity of the 5-HT(3a) receptor from cationic to anionic reveals a conserved feature of the ligand-gated ion channel superfamily.J Biol Chem. 2001 Jun 15;276(24):10977-83. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11439930
-
Molecular determinants of single-channel conductance and ion selectivity in the Cys-loop family: insights from the 5-HT3 receptor.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2005 Nov;26(11):587-94. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2005.09.011. Epub 2005 Sep 27. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2005. PMID: 16194573 Review.
-
The transmembrane domain of the 5-HT3 receptor: its role in selectivity and gating.Biochem Soc Trans. 2004 Jun;32(Pt3):535-9. doi: 10.1042/BST0320535. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004. PMID: 15157179 Review.
Cited by
-
Two rare variations, D478N and D478E, that occur at the same amino acid residue in nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) α2 subunit influence nAChR function.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Oct;85:471-81. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.05.014. Epub 2014 Jun 17. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24950454 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of 5-HT3 receptor mutations identified in schizophrenic patients.J Mol Neurosci. 2006;30(3):273-81. doi: 10.1385/JMN:30:3:273. J Mol Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17401153 Free PMC article.
-
5-HT(3) receptors.J Biol Chem. 2012 Nov 23;287(48):40239-45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R112.406496. Epub 2012 Oct 4. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23038271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modular design of Cys-loop ligand-gated ion channels: functional 5-HT3 and GABA rho1 receptors lacking the large cytoplasmic M3M4 loop.J Gen Physiol. 2008 Feb;131(2):137-46. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200709896. J Gen Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18227272 Free PMC article.
-
The 5-HT3 receptor as a therapeutic target.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2007 Apr;11(4):527-40. doi: 10.1517/14728222.11.4.527. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2007. PMID: 17373882 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- AIDLEY D.J., STANFIELD P.R. Ion Channels, Molecules in Action. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1996.
-
- BARRY P.H., LYNCH J.W. Liquid junction potentials and small cell effects in patch-clamp analysis. J. Membr. Biol. 1991;121:101–117. - PubMed
-
- BREJC K., VAN DIJK W.J., KLAASSEN R.V., SCHUURMANS M., VAN DER OOST J., SMIT A.B., SIXMA T.K. Crystal structure of an ACh-binding protein reveals the ligand-binding domain of nicotinic receptors. Nature. 2001;411:269–276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

