NANC inhibitory neurotransmission in mouse isolated stomach: involvement of nitric oxide, ATP and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide
- PMID: 12970100
- PMCID: PMC1574027
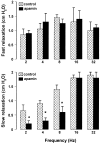
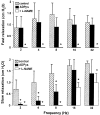
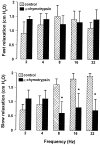
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705431
NANC inhibitory neurotransmission in mouse isolated stomach: involvement of nitric oxide, ATP and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide
Abstract
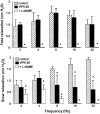
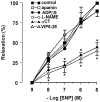
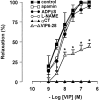
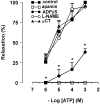
1. The neurotransmitters involved in NANC relaxation and their possible interactions were investigated in mouse isolated stomach, recording the motor responses as changes of endoluminal pressure from whole organ. 2. Field stimulation produced tetrodotoxin-sensitive, frequency-dependent, biphasic responses: rapid transient relaxation followed by a delayed inhibitory component. 3. The inhibitor of the synthesis of nitric oxide (NO), l-NAME, abolished the rapid relaxation and significantly reduced the slow relaxation. Apamin, blocker of Ca2+-dependent K+ channels, or ADPbetaS, which desensitises P2y purinoceptors, reduced the slow relaxation to 2-8 Hz, without affecting that to 16-32 Hz or the fast relaxation. alpha-Chymotrypsin or vasoactive intestinal polypeptide 6-28 (VIP6-28), antagonist of VIP receptors, failed to affect the fast component or the delayed relaxation to 2-4 Hz, but antagonised the slow component to 8-32 Hz. 4. Relaxation to sodium nitroprusside was not affected by l-NAME, apamin or ADPbetaS, but was reduced by alpha-chymotrypsin or VIP6-28. Relaxation to VIP was abolished by alpha-chymotrypsin, antagonised by VIP6-28, but was not affected by l-NAME, apamin or ADPbetaS. Relaxation to ATP was abolished by apamin, antagonised by ADPbetaS, but was not affected by l-NAME or alpha-chymotrypsin. 5. The present results suggest that NO is responsible for the rapid relaxation and partly for the slow relaxation. ATP is involved in the slow relaxation evoked by low frequencies of stimulation. VIP is responsible for the slow relaxation evoked by high frequencies of stimulation. The different neurotransmitters appear to work in parallel, although NO could serve also as a neuromodulator that facilitates release of VIP.
Figures
References
-
- ABRAHAMSSON H. Studies on the inhibitory nervous control of gastric motility. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1973;390:1–38. - PubMed
-
- ALLESCHER H.D., KURJAK M., HUBER A., TRUDRUNG P., SCHUSDZIARRA V. Regulation of VIP release from rat enteric nerve terminals: evidence for a stimulatory effect of NO. Am. J. Physiol. 1996;271:G568–G574. - PubMed
-
- BACCARI M.C., ROMAGNANI P., CALAMAI F. Impaired nitrergic relaxations in the gastric fundus of dystrophic (mdx) mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2000;282:105–108. - PubMed
-
- BARBIER A.J., LEFEBVRE R.A. Involvement of the L-arginine: nitric oxide pathway in nonadrenergic noncholinergic relaxation of the cat gastric fundus. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1993;266:172–178. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

