Inhibition of guinea-pig and human sensory nerve activity and the cough reflex in guinea-pigs by cannabinoid (CB2) receptor activation
- PMID: 12970104
- PMCID: PMC1574031
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705435
Inhibition of guinea-pig and human sensory nerve activity and the cough reflex in guinea-pigs by cannabinoid (CB2) receptor activation
Abstract
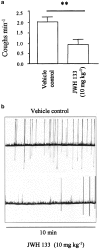
1. There is considerable interest in novel therapies for cough, since currently used agents such as codeine have limited beneficial value due to the associated side effects. Sensory nerves in the airways mediate the cough reflex via activation of C-fibres and RARs. Evidence suggests that cannabinoids may inhibit sensory nerve-mediated responses. 2. We have investigated the inhibitory actions of cannabinoids on sensory nerve depolarisation mediated by capsaicin, hypertonic saline and PGE2 on isolated guinea-pig and human vagus nerve preparations, and the cough reflex in conscious guinea-pigs. 3. The non-selective cannabinoid (CB) receptor agonist, CP 55940, and the selective CB2 agonist, JWH 133 inhibited sensory nerve depolarisations of the guinea-pig vagus nerve induced by hypertonic saline, capsaicin and PGE2. These responses were abolished by the CB2 receptor antagonist SR144528, and unaffected by the CB1 antagonist SR141716A. Similarly, JWH 133 inhibited capsaicin-evoked nerve depolarisations in the human vagus nerve, and was prevented by SR144528. 4. Using a guinea-pig in vivo model of cough, JWH 133 (10 mg kg-1, i.p., 20 min) significantly reduced citric acid-induced cough in conscious guinea pigs compared to those treated with the vehicle control. 5. These data show that activation of the CB2 receptor subtype inhibits sensory nerve activation of guinea-pig and human vagus nerve, and the cough reflex in guinea-pigs, suggesting that the development of CB2 agonists, devoid of CB1-mediated central effects, will provide a new and safe antitussive treatment for chronic cough.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Inhibitory activity of the novel CB2 receptor agonist, GW833972A, on guinea-pig and human sensory nerve function in the airways.Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Oct;155(4):547-57. doi: 10.1038/bjp.2008.298. Epub 2008 Aug 11. Br J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18695648 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effects of CB1 and CB2 receptor agonists on responses of DRG neurons and dorsal horn neurons in neuropathic rats.Eur J Neurosci. 2005 Jul;22(2):371-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04206.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16045490
-
Cannabinoid CB2 receptor activation inhibits mechanically evoked responses of wide dynamic range dorsal horn neurons in naïve rats and in rat models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain.Eur J Neurosci. 2004 Nov;20(9):2311-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03690.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15525273
-
Physiology and plasticity of putative cough fibres in the Guinea pig.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2002;15(3):193-8. doi: 10.1006/pupt.2002.0362. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2002. PMID: 12099763 Review.
-
Pharmacophores for ligand recognition and activation/inactivation of the cannabinoid receptors.Curr Pharm Des. 2003;9(20):1607-33. doi: 10.2174/1381612033454577. Curr Pharm Des. 2003. PMID: 12871061 Review.
Cited by
-
Central adenosine A1 receptors inhibit cough via suppression of excitatory glutamatergic and tachykininergic neurotransmission.Br J Pharmacol. 2018 Aug;175(15):3162-3174. doi: 10.1111/bph.14360. Epub 2018 Jun 19. Br J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29767468 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabinoids inhibit cholinergic contraction in human airways through prejunctional CB1 receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Jun;171(11):2767-77. doi: 10.1111/bph.12597. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24467410 Free PMC article.
-
Antitussive drugs--past, present, and future.Pharmacol Rev. 2014 Mar 26;66(2):468-512. doi: 10.1124/pr.111.005116. Print 2014. Pharmacol Rev. 2014. PMID: 24671376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sensitization of capsaicin and icilin responses in oxaliplatin treated adult rat DRG neurons.Mol Pain. 2010 Nov 24;6:82. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-6-82. Mol Pain. 2010. PMID: 21106058 Free PMC article.
-
The Therapeutic Potential of Cannabis in Counteracting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation.Molecules. 2021 Jul 28;26(15):4551. doi: 10.3390/molecules26154551. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34361704 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- BELVISI M.G., VENKATESAN P., BARNES P.J., FOX A.J. A comparison of the chemosensitivity of the isolated guinea-pig and human vagus nerves. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998;157:A487.
-
- CALIGNANO A., CATONA I., DESARNAUD F., GIUFFRIDA A., LA RANA G., MACKIE K., FREUND T.F., PIOMELLI D. Bidirectional control of airway responsiveness by cannabinoids. Nature. 2000;408:96–101. - PubMed
-
- CANNING B.J. Interactions between vagal afferent nerve subtypes mediating cough. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002;15:187–192. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

