Spinal administration of lipoxygenase inhibitors suppresses behavioural and neurochemical manifestations of naloxone-precipitated opioid withdrawal
- PMID: 12970109
- PMCID: PMC1574036
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705440
Spinal administration of lipoxygenase inhibitors suppresses behavioural and neurochemical manifestations of naloxone-precipitated opioid withdrawal
Abstract
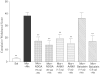
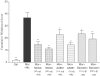
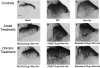
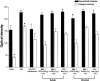
1. This study investigated the role of spinal lipoxygenase (LOX) products in the induction and expression of opioid physical dependence using behavioural assessment of withdrawal and immunostaining for CGRP and Fos protein expression in the spinal cord. 2. Administration of escalating doses (5-50 mg kg-1; i.p.) of morphine for 5 days markedly elevated CGRP-like immunoreactivity in the dorsal horn of the rat spinal cord. Naloxone (2 mg kg-1; i.p.) challenge precipitated a robust withdrawal syndrome that depleted CGRP-like immunoreactivity and increased the number of Fos-like immunoreactive neurons in the dorsal horn. 3. Intrathecal administration of NDGA (10, 20 microg), a nonselective LOX inhibitor, AA-861 (1.5, 3 microg), a 5-LOX selective inhibitor, or baicalein (1.4, 2.8 microg), a 12-LOX selective inhibitor, concurrently with systemic morphine for 5 days or as a single injection immediately preceding naloxone challenge, blocked the depletion of CGRP-like immunoreactivity, prevented increase in the number of Fos-like immunoreactive neurons in the dorsal horn, and significantly attenuated the morphine withdrawal syndrome. 4. The results of this study suggest that activity of LOX products, at the spinal level, contributes to the expression of opioid physical dependence, and that this activity may be expressed through increased sensory neuropeptide release.
Figures


References
-
- ABBADIE C., HONORE P., FOURNIE-ZALUSKI M.C., ROQUES B.P., BESSON J.M. Effects of opioids and non-opioids on c-Fos-like immunoreactivity induced in rat lumbar spinal cord neurons by noxious heat stimulation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1994;258:215–227. - PubMed
-
- BENO D.W., MULLEN J., DAVIS B.H. Lipoxygenase inhibitors block PDGF-induced mitogenesis: a MAPK-independent mechanism that blocks fos and egr. Am. J. Physiol. 1995;268:C604–C610. - PubMed
-
- CAPASSO A. Further studies on the involvement of the arachidonic acid cascade in the acute dependence produced by mu, kappa and delta opioid agonists in isolated tissues. Neuropharmacology. 1999;38:871–877. - PubMed
-
- CARLTON S.M., WESTLUND K.N., ZHANG D.X., SORKIN L.S., WILLIS W.D. Calcitonin gene-related peptide containing primary afferent fibers synapse on primate spinothalamic tract cells. Neurosci. Lett. 1990;109:76–81. - PubMed
-
- CHIENG B., KEAY K.A., CHRISTIE M.J. Increased fos-like immunoreactivity in the periaqueductal gray of anaesthetised rats during opiate withdrawal. Neurosci. Lett. 1995;183:79–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

