Scavenger receptor class B type I (SR-BI) in pig enterocytes: trafficking from the brush border to lipid droplets during fat absorption
- PMID: 12970134
- PMCID: PMC1773834
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.52.10.1424
Scavenger receptor class B type I (SR-BI) in pig enterocytes: trafficking from the brush border to lipid droplets during fat absorption
Abstract
Background: Scavenger receptor class B type I (SR-BI) is known to mediate cellular uptake of cholesterol from high density lipoprotein particles and is particularly abundant in liver and steroidogenic tissues. In addition, SR-BI expression in the enterocyte brush border has also been reported but its role in the small intestine remains unclear.
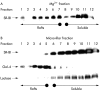
Aim and methods: To gain insight into the possible function of pig SR-BI during uptake of dietary fat, its localisation in enterocytes was studied in the fasting state and during fat absorption by immunogold electron microscopy and subcellular fractionation.
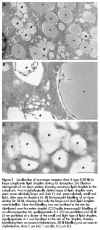
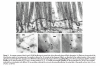
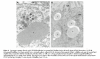
Results: In the fasting state, SR-BI was mainly localised in the microvillar membrane and in apical invaginations/pits between adjacent microvilli. In addition, a subapical compartment and small cytoplasmic lipid droplets were distinctly labelled. During lipid absorption, the receptor was found in clathrin positive apical coated pits and vesicles. In addition, cytoplasmic lipid droplets that greatly increased in size and number were strongly labelled by the SR-BI antibody whereas apolipoprotein A-1 positive chylomicrons were largely devoid of the receptor.
Conclusion: During absorption of dietary fat, SR-BI is endocytosed from the enterocyte brush border and accumulates in cytoplasmic lipid droplets. Internalisation of the receptor occurs mainly by clathrin coated pits rather than by a caveolae/lipid raft based mechanism.
Figures

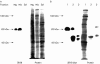

References
-
- Krieger M. Charting the fate of the “good cholesterol”: identification and characterization of the high-density lipoprotein receptor SR-BI. Annu Rev Biochem 1999;68:523–58. - PubMed
-
- Silver DL, Tall AR. The cellular biology of scavenger receptor class B type I. Curr Opin Lipidol 2001;12:497–504. - PubMed
-
- Acton SL, Scherer PE, Lodish HF, et al. Expression cloning of SR-BI, a CD36-related class B scavenger receptor. J Biol Chem 1994;269:21003–9. - PubMed
-
- Trigatti BL, Rigotti A, Braun A. Cellular and physiological roles of SR-BI, a lipoprotein receptor which mediates selective lipid uptake. Biochim Biophys Acta 2000;1529:276–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
