The dendritic cell: its role in intestinal inflammation and relationship with gut bacteria
- PMID: 12970149
- PMCID: PMC1773829
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.52.10.1522
The dendritic cell: its role in intestinal inflammation and relationship with gut bacteria
Abstract
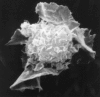
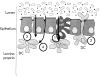
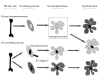
Dendritic cells are antigen presenting cells that are likely to be pivotal in the balance between tolerance and active immunity to commensal microorganisms that is fundamental to inflammatory conditions, including Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Interactions between dendritic cells and microbial products are discussed and how they contribute to regulation of immune responses. The concept that interactions between dendritic cells and commensal organisms may be responsible for maintaining intestinal immune homeostasis is also explored.
Figures



References
-
- Banchereau J, Briere F, Caux C, et al. Immunobiology of dendritic cells. Annu Rev Immunol 2000;18:767–811. - PubMed
-
- Heath WR, Carbone FR. Cross-presentation, dendritic cells, tolerance and immunity. Annu Rev Immunol 2001;19:47–64. - PubMed
-
- Liu YJ. Dendritic cell subsets and lineages, and their functions in innate and adaptive immunity. Cell 2001;106:259–62. - PubMed
-
- Moser M, Murphy KM. Dendritic cell regulation of TH1-TH2 development. Nat Immunol 2000;1:199–205. - PubMed
-
- Shortman K, Liu YJ. Mouse and human dendritic cell subtypes. Nature Rev Immunol 2002;2:151–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
