Amplification of receptor signalling by Ca2+ entry-mediated translocation and activation of PLCgamma2 in B lymphocytes
- PMID: 12970180
- PMCID: PMC212724
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg457
Amplification of receptor signalling by Ca2+ entry-mediated translocation and activation of PLCgamma2 in B lymphocytes
Abstract
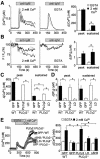
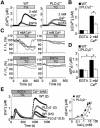
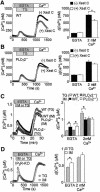
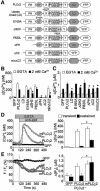
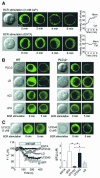
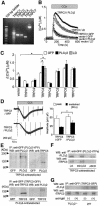
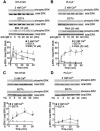
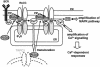
In non-excitable cells, receptor-activated Ca2+ signalling comprises initial transient responses followed by a Ca2+ entry-dependent sustained and/or oscillatory phase. Here, we describe the molecular mechanism underlying the second phase linked to signal amplification. An in vivo inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) sensor revealed that in B lymphocytes, receptor-activated and store-operated Ca2+ entry greatly enhanced IP3 production, which terminated in phospholipase Cgamma2 (PLCgamma2)-deficient cells. Association between receptor-activated TRPC3 Ca2+ channels and PLCgamma2, which cooperate in potentiating Ca2+ responses, was demonstrated by co-immunoprecipitation. PLCgamma2-deficient cells displayed diminished Ca2+ entry-induced Ca2+ responses. However, this defect was canceled by suppressing IP3-induced Ca2+ release, implying that IP3 and IP3 receptors mediate the second Ca2+ phase. Furthermore, confocal visualization of PLCgamma2 mutants demonstrated that Ca2+ entry evoked a C2 domain-mediated PLCgamma2 translocation towards the plasma membrane in a lipase-independent manner to activate PLCgamma2. Strikingly, Ca2+ entry-activated PLCgamma2 maintained Ca2+ oscillation and extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation downstream of protein kinase C. We suggest that coupling of Ca2+ entry with PLCgamma2 translocation and activation controls the amplification and co-ordination of receptor signalling.
Figures

References
-
- Ananthanarayanan B., Das,S., Rhee,S.G., Murray,D. and Cho,W. (2002) Membrane targeting of C2 domains of phospholipase C-δ isoforms. J. Biol. Chem., 277, 3568–3575. - PubMed
-
- Bae Y.S., Cantley,L.G., Chen,C.S., Kim,S.R., Kwon,K.S. and Rhee,S.G. (1998) Activation of phospholipase C-γ by phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. J. Biol. Chem., 273, 4465–4469. - PubMed
-
- Bairoch A. and Cox,J.A. (1990) EF-hand motifs in inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C. FEBS Lett., 269, 454–456. - PubMed
-
- Berridge M.J. (1993) Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature, 361, 315–325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

