The vpu protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 plays a protective role against virus-induced apoptosis in primary CD4(+) T lymphocytes
- PMID: 12970415
- PMCID: PMC228500
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.19.10304-10313.2003
The vpu protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 plays a protective role against virus-induced apoptosis in primary CD4(+) T lymphocytes
Abstract
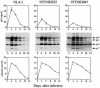
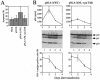
Previous data revealed that primary cultures of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were killed by apoptosis at higher rates after infection with two CRF01_AE primary isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) than after infection with five other CRF01_AE primary isolates, five subtype B primary isolates, and two subtype B laboratory strains. Here, we show evidence that mutations at the vpu gene which were exclusively identified only in the two CRF01_AE isolates mentioned above are involved in their abilities to induce massive apoptosis in primary CD4(+) T lymphocytes. The rates of virus production by these two isolates in the culture media of infected PBMCs were lower (the same as those of the other CRF01_AE isolates) than those of the subtype B isolates. To confirm the correlation between the higher apoptosis-inducing abilities and the mutations at the vpu gene, infectious molecular clone pNL4-3-based vpu mutants were constructed and examined for their apoptosis induction levels. The apoptosis induction levels after introduction of the vpu mutations were greatly increased in primary CD4(+) T lymphocytes. In contrast, the apoptosis induction abilities of these vpu mutants were lower in human T-cell line MT-4. Thus, the Vpu protein of HIV-1 could play a protective role against virus-induced apoptosis in primary CD4(+) T lymphocytes.
Figures




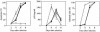
Similar articles
-
Higher frequency of premature stop codon mutations at vpu gene of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 CRF01_AE compared with those of other subtypes.Microbes Infect. 2005 Feb;7(2):139-47. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2004.09.017. Epub 2005 Jan 4. Microbes Infect. 2005. PMID: 15715990
-
Augmentation of virus secretion by the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vpu protein is cell type independent and occurs in cultured human primary macrophages and lymphocytes.J Virol. 1995 Dec;69(12):7699-711. doi: 10.1128/JVI.69.12.7699-7711.1995. J Virol. 1995. PMID: 7494279 Free PMC article.
-
Function of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vpu protein in various cell types.J Gen Virol. 1995 Nov;76 ( Pt 11):2717-22. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-76-11-2717. J Gen Virol. 1995. PMID: 7595378
-
Various plus unique: Viral protein U as a plurifunctional protein for HIV-1 replication.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017 Apr;242(8):850-858. doi: 10.1177/1535370217697384. Epub 2017 Jan 1. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017. PMID: 28346011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vpu protein: roles in virus release and CD4 downregulation.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1995;193:107-20. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-78929-8_6. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7648871 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Detection of the HIV-1 Accessory Proteins Nef and Vpu by Flow Cytometry Represents a New Tool to Study Their Functional Interplay within a Single Infected CD4+ T Cell.J Virol. 2022 Mar 23;96(6):e0192921. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01929-21. Epub 2022 Jan 26. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35080425 Free PMC article.
-
Human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1)-mediated apoptosis: new therapeutic targets.Viruses. 2014 Aug 19;6(8):3181-227. doi: 10.3390/v6083181. Viruses. 2014. PMID: 25196285 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Auwanit, W., T. Mukai, P. I. N. Ayuthaya, T. Kurata, and K. Ikuta. 2001. Full-length sequences of two subtype E HIV-1 isolates from 1995 samples of patients with sexually transmitted diseases in Thailand. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 17:867-871. - PubMed
-
- Badley, A. D., A. A. Pilon, A. Landay, and D. H. Lynch. 2000. Mechanisms of HIV-associated lymphocyte apoptosis. Blood 96:2951-2964. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

