Identification of the receptor binding domain of the mouse mammary tumor virus envelope protein
- PMID: 12970432
- PMCID: PMC228533
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.19.10468-10478.2003
Identification of the receptor binding domain of the mouse mammary tumor virus envelope protein
Abstract
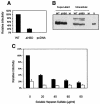
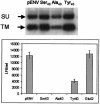
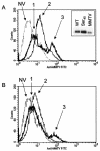
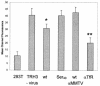
Mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV) is a betaretrovirus that infects rodent cells and uses mouse transferrin receptor 1 for cell entry. To characterize the interaction of MMTV with its receptor, we aligned the MMTV envelope surface (SU) protein with that of Friend murine leukemia virus (F-MLV) and identified a putative receptor-binding domain (RBD) that included a receptor binding sequence (RBS) of five amino acids and a heparin-binding domain (HBD). Mutation of the HBD reduced virus infectivity, and soluble heparan sulfate blocked infection of cells by wild-type pseudovirus. Interestingly, some but not all MMTV-like elements found in primary and cultured human breast cancer cell lines, termed h-MTVs, had sequence alterations in the putative RBS. Single substitution of one of the amino acids found in an h-MTV RBS variant in the RBD of MMTV, Phe(40) to Ser, did not alter species tropism but abolished both virus binding to cells and infectivity. Neutralizing anti-SU monoclonal antibodies also recognized a glutathione S-transferase fusion protein that contained the five-amino-acid RBS region from MMTV. The critical Phe(40) residue is located on a surface of the MMTV RBD model that is distant from and may be structurally more rigid than the region of F-MLV RBD that contains its critical binding site residues. This suggests that, in contrast to other murine retroviruses, binding to its receptor may result in few or no changes in MMTV envelope protein conformation.
Figures



References
-
- Bernard, K. A., W. B. Klimstra, and R. E. Johnston. 2000. Mutations in the E2 glycoprotein of Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus confer heparan sulfate interaction, low morbidity, and rapid clearance from blood of mice. Virology 276:93-103. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein, H. J. 2000. Recent changes to RasMol, recombining the variants. Trends Biochem. Sci. 25:453-455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

