Biochemical and genetic characterizations of a novel human immunodeficiency virus type 1 inhibitor that blocks gp120-CD4 interactions
- PMID: 12970437
- PMCID: PMC228513
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.19.10528-10536.2003
Biochemical and genetic characterizations of a novel human immunodeficiency virus type 1 inhibitor that blocks gp120-CD4 interactions
Abstract
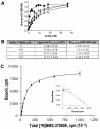
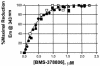
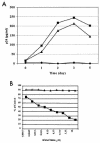
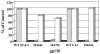
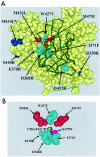
BMS-378806 is a recently discovered small-molecule human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) attachment inhibitor with good antiviral activity and pharmacokinetic properties. Here, we demonstrate that the compound targets viral entry by inhibiting the binding of the HIV-1 envelope gp120 protein to cellular CD4 receptors via a specific and competitive mechanism. BMS-378806 binds directly to gp120 at a stoichiometry of approximately 1:1, with a binding affinity similar to that of soluble CD4. The potential BMS-378806 target site was localized to a specific region within the CD4 binding pocket of gp120 by using HIV-1 gp120 variants carrying either compound-selected resistant substitutions or gp120-CD4 contact site mutations. Mapping of resistance substitutions to the HIV-1 envelope, and the lack of compound activity against a CD4-independent viral infection confirm the gp120-CD4 interactions as the target in infected cells. BMS-378806 therefore serves as a prototype for this new class of antiretroviral agents and validates gp120 as a viable target for small-molecule inhibitors.
Figures


References
-
- Blair, W. S., P. F. Lin, N. A. Meanwell, and P. B. Wallace. 2000. HIV-1 entry-an expanding portal for drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 5:183-194. - PubMed
-
- Campbell, I. D., and R. A. Dwek. 1984. Biological spectroscopy. Benjamin/Cummings, Menlo Park, Calif.
-
- Chan, D. C., and P. S. Kim. 1998. HIV entry and its inhibition. Cell 93:681-684. - PubMed
-
- Cohen, O. J., and A. S. Fauci. 2001. Current strategies in the treatment of HIV infection. Adv. Intern. Med. 46:207-246. - PubMed
-
- Copeland, R. A. 2000. A practical introduction to structure, mechanism, and data analysis, p. 104. In V. C. H. Wiley (ed.), Enzymes, 2nd ed. John Wiley & Sons, New York, N.Y.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

