Inhibitory effects of c9, t11-conjugated linoleic acid on invasion of human gastric carcinoma cell line SGC-7901
- PMID: 12970874
- PMCID: PMC4656642
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i9.1909
Inhibitory effects of c9, t11-conjugated linoleic acid on invasion of human gastric carcinoma cell line SGC-7901
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effect of c9, t11-conjugated linoleic acid (c9, t11-CLA) on the invasion of human gastric carcinoma cell line and its possible mechanism of preventing metastasis.
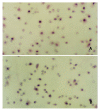
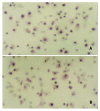
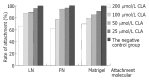
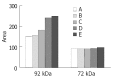
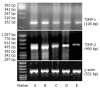
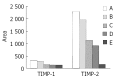
Methods: Using reconstituted basement membrane invasion, chemotaxis, adhesion, PAGE substrate zymography and RT-PCR assays, we analyzed the abilities of invasion, direct migration, adhesion of intracellular matrix, as well as the activity of type IV collagenase and expression of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP)-1 and TIMP-2 mRNA in SGC-7901 cells which were treated with gradually increased concentrations (25, 50, 100 and 200 micromol/L) of c9, t11-CLA for 24 h.
Results: At the concentrations of 200 micromol/L, 100 micromol/L and 50 micromol/L, c9,t11-CLA suppressed the invasion of SGC-7901 cells into the reconstituted basement membrane by 53.7 %, 40.9 % and 29.3 %, respectively, in comparison with the negative control. Only in the 200 micromol/L c9,t11-CLA group, the chemotaxis of SGC-7901 cells was inhibited by 16.0 % in comparison with the negative control. C9,t11-CLA also could inhibit the adhesion of SGC-7901 cells to laminin, fibronectin and Matrigel, increase the expression of TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 mRNA, and reduce type IV collagenase activities in the serum-free medium supernatant of SGC-7901 cells.
Conclusion: c9,t11-CLA can inhibit the invasion of SGC-7901 cells at multiple procedures in tumor metastasis cascade, which may be associated with the induction of TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 mRNA expression.
Figures

References
-
- Sébédio JL, Gnaedig S, Chardigny JM. Recent advances in conjugated linoleic acid research. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 1999;2:499–506. - PubMed
-
- Pariza MW, Park Y, Cook ME. Mechanisms of action of conjugated linoleic acid: evidence and speculation. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 2000;223:8–13. - PubMed
-
- Pariza MW, Park Y, Cook ME. Conjugated linoleic acid and the control of cancer and obesity. Toxicol Sci. 1999;52:107–110. - PubMed
-
- Whigham LD, Cook ME, Atkinson RL. Conjugated linoleic acid: implications for human health. Pharmacol Res. 2000;42:503–510. - PubMed
-
- MacDonald HB. Conjugated linoleic acid and disease prevention: a review of current knowledge. J Am Coll Nutr. 2000;19:111S–118S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

