Kangxian ruangan keli inhibits hepatic stellate cell proliferation mediated by PDGF
- PMID: 12970904
- PMCID: PMC4656672
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i9.2050
Kangxian ruangan keli inhibits hepatic stellate cell proliferation mediated by PDGF
Abstract
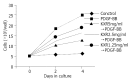
Aim: To investigate the effect of Kangxian ruangan keli (KXR) on hepatic stellate cell (HSC) proliferation mediated by platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and the underlying mechanism.
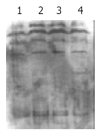
Methods: In a serum-free culture system, HSCs were treated with a KXR preparation for 24 hours, followed by stimulation with PDGF-BB for 24 hours. Then the cells were incubated again in the medium containing KXR for 3 hours stimulated with PDGF-BB for 5 minutes, and collected. The proliferation of HSC was examined using an MTT assay and flow cytometry. Tyrosine phosphorylation was detected with Western blotting and visualized by the enhanced chemiluminescent (ECL) method.
Results: The OD values for the HSCs growing in the media without and with addition of PDGF were 0.17+/-0.06 and 0.82+/-0.05, respectively. The PDGF-induced increase was hindered remarkably by KXR preparation in a dose-dependent manner. The reaction values for the systems with 5 mg/mL, 2.5 mg/mL and 1.25 mg/mL of KXR were 0.28+/-0.03, 0.37+/-0.02 and 0.43+/-0.04, respectively. Moreover, the percentages of S-phase cells in these KXR-containing culture systems were 10.95+/-1.35, 32.76+/-1.07 and 43.19+/-1.09, respectively, all of which were significantly lower than that in the culture free of KXR (68.24+/-2.72). In addition, the values for tyrosine-phosphorylated protein in HSCs treated with 5 mg/mL and 1.25 mg/mL of KXR were 0.1349+/-0.0072 and 0.1658+/-0.0025, respectively, which were smaller than that in the cells treated only with PDGF-BB (0.1813+/-0.0117).
Conclusion: Within the dose range used in the present study, KXR preparation shows an inhibitory effect on HSC proliferation induced by PDGF. The mechanism of this process may involve interference with tyrosine phosphorylation mediated by PDGF.
Figures
References
-
- Friedman SL. Cytokines and fibrogenesis. Semin Liver Dis. 1999;19:129–140. - PubMed
-
- Jiang HQ, Zhang XL. Progress in the study of pathogenesis in hepatic fibrosis. Shijie Huangren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2000;8:687–689.
-
- Reeves HL, Friedman SL. Activation of hepatic stellate cells--a key issue in liver fibrosis. Front Biosci. 2002;7:d808–d826. - PubMed
-
- Pinzani M, Marra F, Carloni V. Signal transduction in hepatic stellate cells. Liver. 1998;18:2–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

