Survival and effectiveness of leflunomide compared with methotrexate and sulfasalazine in rheumatoid arthritis: a matched observational study
- PMID: 12972472
- PMCID: PMC1754333
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.62.10.944
Survival and effectiveness of leflunomide compared with methotrexate and sulfasalazine in rheumatoid arthritis: a matched observational study
Abstract
Objective: To determine the survival and clinical effectiveness of leflunomide (LEF) compared with methotrexate (MTX) and sulfasalazine (SSZ) for RA in an observational study.
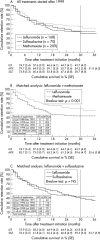
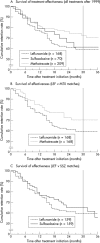
Methods: An observational database of 1088 patients and 5141 patient years of DMARD treatment (2680 courses) from two academic hospitals was filtered for treatment with LEF, MTX, and SSZ. LEF treatment groups were matched for patients' age, baseline ESR, number of previous DMARDs, and hospital cohort with MTX and SSZ treatment groups. For these treatments, Kaplan-Meier analyses of time until the drug was discontinued (drug "survival"), and the effectiveness and safety of continuation of treatment, were performed. The change in disease activity markers (CRP, ESR) was compared between the groups.
Results: The median dose during the study increased from 10 to 15 mg MTX/week and from 1.5 to 2.0 g SSZ/day. Matched survival analysis showed better retention rates for MTX (mean (SEM) survival 28 (1) months) than for LEF (20 (1) months; p=0.001), whereas retention rates of SSZ (23 (1) months) were similar to those of LEF (p=NS). Treatments were stopped earlier because of adverse events (AEs, 3 months) than because of ineffectiveness (IE, 10 months; p<0.001). LEF and MTX were less likely to be stopped because of AEs than SSZ. LEF courses were stopped earlier for AEs (p<0.001) than MTX.
Conclusions: Current dosing strategies should be re-evaluated, and coping strategies for common AEs should be investigated. This will be necessary to achieve better drug retention of LEF. At present, MTX continues to be the most effective drug in clinical practice.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

