Spy1 interacts with p27Kip1 to allow G1/S progression
- PMID: 12972555
- PMCID: PMC196558
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-12-0820
Spy1 interacts with p27Kip1 to allow G1/S progression
Abstract
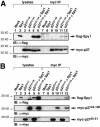
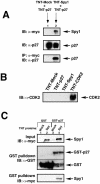
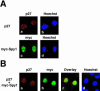
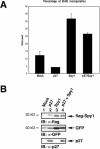
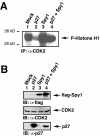
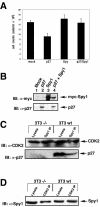
Progression through the G1/S transition commits cells to synthesize DNA. Cyclin dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) is the major kinase that allows progression through G1/S phase and subsequent replication events. p27 is a CDK inhibitor (CKI) that binds to CDK2 to prevent premature activation of this kinase. Speedy (Spy1), a novel cell cycle regulatory protein, has been found to prematurely activate CDK2 when microinjected into Xenopus oocytes and when expressed in mammalian cells. To determine the mechanism underlying Spy1-induced proliferation in mammalian cell cycle regulation, we used human Spy1 as bait in a yeast two-hybrid screen to identify interacting proteins. One of the proteins isolated was p27; this novel interaction was confirmed both in vitro, using bacterially expressed and in vitro translated proteins, and in vivo, through the examination of endogenous and transfected proteins in mammalian cells. We demonstrate that Spy1 expression can overcome a p27-induced cell cycle arrest to allow for DNA synthesis and CDK2 histone H1 kinase activity. In addition, we utilized p27-null cells to demonstrate that the proliferative effect of Spy1 depends on the presence of endogenous p27. Our data suggest that Spy1 associates with p27 to promote cell cycle progression through the G1/S transition.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Human Speedy: a novel cell cycle regulator that enhances proliferation through activation of Cdk2.J Cell Biol. 2002 Apr 29;157(3):357-66. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200109045. Epub 2002 Apr 29. J Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11980914 Free PMC article.
-
Spy1 enhances phosphorylation and degradation of the cell cycle inhibitor p27.Cell Cycle. 2007 Aug 1;6(15):1937-45. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.15.4520. Epub 2007 May 30. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 17671428
-
Vitamin D inhibits G1 to S progression in LNCaP prostate cancer cells through p27Kip1 stabilization and Cdk2 mislocalization to the cytoplasm.J Biol Chem. 2003 Nov 21;278(47):46862-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M306340200. Epub 2003 Sep 3. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12954644
-
Cdk2 as a master of S phase entry: fact or fake?Cell Cycle. 2004 Jan;3(1):35-7. Cell Cycle. 2004. PMID: 14657662 Review.
-
Targeting cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) interactions with cyclins and Speedy 1 (Spy1) for cancer and male contraception.Future Med Chem. 2025 Mar;17(5):607-627. doi: 10.1080/17568919.2025.2463868. Epub 2025 Mar 4. Future Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40034037 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of a new family of cyclin-dependent kinase activators.Biochem J. 2005 Mar 1;386(Pt 2):349-55. doi: 10.1042/BJ20041779. Biochem J. 2005. PMID: 15574121 Free PMC article.
-
Regulated Pumilio-2 binding controls RINGO/Spy mRNA translation and CPEB activation.Genes Dev. 2006 Jan 15;20(2):199-209. doi: 10.1101/gad.1383106. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 16418484 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis of divergent cyclin-dependent kinase activation by Spy1/RINGO proteins.EMBO J. 2017 Aug 1;36(15):2251-2262. doi: 10.15252/embj.201796905. Epub 2017 Jun 30. EMBO J. 2017. PMID: 28666995 Free PMC article.
-
The atypical cell cycle regulator Spy1 suppresses differentiation of the neuroblastoma stem cell population.Oncoscience. 2014 May 6;1(5):336-48. doi: 10.18632/oncoscience.36. eCollection 2014. Oncoscience. 2014. PMID: 25594028 Free PMC article.
-
The atypical cyclin-like protein Spy1 overrides p53-mediated tumour suppression and promotes susceptibility to breast tumourigenesis.Breast Cancer Res. 2019 Dec 11;21(1):140. doi: 10.1186/s13058-019-1211-3. Breast Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31829284 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baldassarre, G. et al. (2000). Retinoic acid induces neuronal differentiation of embryonal carcinoma cells by reducing proteasome-dependent proteolysis of the cyclin-dependent inhibitor p27. Cell Growth Differ. 11, 517–526. - PubMed
-
- Carrano, A.C., Eytan, E., Hershko, A., and Pagano, M. (1999). SKP2 is required for ubiquitin-mediated degradation of the CDK inhibitor p27. Nat. Cell Biol. 4, 193–199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

