RAM: a conserved signaling network that regulates Ace2p transcriptional activity and polarized morphogenesis
- PMID: 12972564
- PMCID: PMC196567
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e03-01-0018
RAM: a conserved signaling network that regulates Ace2p transcriptional activity and polarized morphogenesis
Abstract
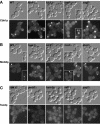
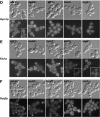
In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, polarized morphogenesis is critical for bud site selection, bud development, and cell separation. The latter is mediated by Ace2p transcription factor, which controls the daughter cell-specific expression of cell separation genes. Recently, a set of proteins that include Cbk1p kinase, its binding partner Mob2p, Tao3p (Pag1p), and Hym1p were shown to regulate both Ace2p activity and cellular morphogenesis. These proteins seem to form a signaling network, which we designate RAM for regulation of Ace2p activity and cellular morphogenesis. To find additional RAM components, we conducted genetic screens for bilateral mating and cell separation mutants and identified alleles of the PAK-related kinase Kic1p in addition to Cbk1p, Mob2p, Tao3p, and Hym1p. Deletion of each RAM gene resulted in a loss of Ace2p function and caused cell polarity defects that were distinct from formin or polarisome mutants. Two-hybrid and coimmunoprecipitation experiments reveal a complex network of interactions among the RAM proteins, including Cbk1p-Cbk1p, Cbk1p-Kic1p, Kic1p-Tao3p, and Kic1p-Hym1p interactions, in addition to the previously documented Cbk1p-Mob2p and Cbk1p-Tao3p interactions. We also identified a novel leucine-rich repeat-containing protein Sog2p that interacts with Hym1p and Kic1p. Cells lacking Sog2p exhibited the characteristic cell separation and cell morphology defects associated with perturbation in RAM signaling. Each RAM protein localized to cortical sites of growth during both budding and mating pheromone response. Hym1p was Kic1p- and Sog2p-dependent and Sog2p and Kic1p were interdependent for localization, indicating a close functional relationship between these proteins. Only Mob2p and Cbk1p were detectable in the daughter cell nucleus at the end of mitosis. The nuclear localization and kinase activity of the Mob2p-Cbk1p complex were dependent on all other RAM proteins, suggesting that Mob2p-Cbk1p functions late in the RAM network. Our data suggest that the functional architecture of RAM signaling is similar to the S. cerevisiae mitotic exit network and Schizosaccharomyces pombe septation initiation network and is likely conserved among eukaryotes.
Figures




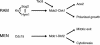
Similar articles
-
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mob2p-Cbk1p kinase complex promotes polarized growth and acts with the mitotic exit network to facilitate daughter cell-specific localization of Ace2p transcription factor.J Cell Biol. 2002 Sep 2;158(5):885-900. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200203094. Epub 2002 Aug 26. J Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12196508 Free PMC article.
-
The Cbk1p pathway is important for polarized cell growth and cell separation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Apr;21(7):2449-62. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.7.2449-2462.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11259593 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of the RAM signaling network in cell cycle progression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Curr Genet. 2006 Jun;49(6):384-92. doi: 10.1007/s00294-006-0069-y. Epub 2006 Mar 22. Curr Genet. 2006. PMID: 16552603
-
The RAM network in pathogenic fungi.Eukaryot Cell. 2012 Jun;11(6):708-17. doi: 10.1128/EC.00044-12. Epub 2012 Apr 27. Eukaryot Cell. 2012. PMID: 22544903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MOB control: reviewing a conserved family of kinase regulators.Cell Signal. 2011 Sep;23(9):1433-40. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.04.007. Epub 2011 Apr 21. Cell Signal. 2011. PMID: 21539912 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Statistical approaches to use a model organism for regulatory sequences annotation of newly sequenced species.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e42489. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042489. Epub 2012 Sep 11. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22984403 Free PMC article.
-
Microtubule integrity regulates budding yeast RAM pathway gene expression.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Sep 12;10:989820. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.989820. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36172269 Free PMC article.
-
The NDR kinase scaffold HYM1/MO25 is essential for MAK2 map kinase signaling in Neurospora crassa.PLoS Genet. 2012 Sep;8(9):e1002950. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002950. Epub 2012 Sep 20. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 23028357 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-templated predictions of novel protein interactions from sequence information.PLoS Comput Biol. 2007 Sep;3(9):1783-9. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030182. PLoS Comput Biol. 2007. PMID: 17892321 Free PMC article.
-
From function to shape: a novel role of a formin in morphogenesis of the fungus Ashbya gossypii.Mol Biol Cell. 2006 Jan;17(1):130-45. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-06-0479. Epub 2005 Oct 19. Mol Biol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16236798 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

