The ubiquitin-associated domain of hPLIC-2 interacts with the proteasome
- PMID: 12972570
- PMCID: PMC196580
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-11-0766
The ubiquitin-associated domain of hPLIC-2 interacts with the proteasome
Abstract
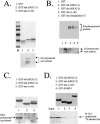
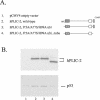
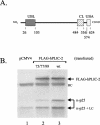
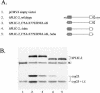
The ubiquitin-like hPLIC proteins can associate with proteasomes, and hPLIC overexpression can specifically interfere with ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (Kleijnen et al., 2000). Because the hPLIC proteins can also interact with certain E3 ubiquitin protein ligases, they may provide a link between the ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation machineries. The amino-terminal ubiquitin-like (ubl) domain is a proteasome-binding domain. Herein, we report that there is a second proteasome-binding domain in hPLIC-2: the carboxyl-terminal ubiquitin-associated (uba) domain. Coimmunoprecipitation experiments of wild-type and mutant hPLIC proteins revealed that the ubl and uba domains each contribute independently to hPLIC-2-proteasome binding. There is specificity for the interaction of the hPLIC-2 uba domain with proteasomes, because uba domains from several other proteins failed to bind proteasomes. Furthermore, the binding of uba domains to polyubiquitinated proteins does not seem to be sufficient for the proteasome binding. Finally, the uba domain is necessary for the ability of full-length hPLIC-2 to interfere with the ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis of p53. The PLIC uba domain has been reported to bind and affect the functions of proteins such as GABAA receptor and presenilins. It is possible that the function of these proteins may be regulated or mediated through proteasomal degradation pathways.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The hPLIC proteins may provide a link between the ubiquitination machinery and the proteasome.Mol Cell. 2000 Aug;6(2):409-19. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)00040-x. Mol Cell. 2000. PMID: 10983987
-
Structural studies of the interaction between ubiquitin family proteins and proteasome subunit S5a.Biochemistry. 2002 Feb 12;41(6):1767-77. doi: 10.1021/bi011892y. Biochemistry. 2002. PMID: 11827521
-
Proteasome subunit Rpn1 binds ubiquitin-like protein domains.Nat Cell Biol. 2002 Sep;4(9):725-30. doi: 10.1038/ncb845. Nat Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12198498
-
From UBA to UBX: new words in the ubiquitin vocabulary.Trends Cell Biol. 2002 May;12(5):216-21. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(02)02269-9. Trends Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12062168 Review.
-
Ubiquitin-like and ubiquitin-associated domain proteins: significance in proteasomal degradation.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009 Sep;66(17):2819-33. doi: 10.1007/s00018-009-0048-9. Epub 2009 May 26. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009. PMID: 19468686 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ubiquilin regulates presenilin endoproteolysis and modulates gamma-secretase components, Pen-2 and nicastrin.Biochem J. 2005 Nov 1;391(Pt 3):513-25. doi: 10.1042/BJ20050491. Biochem J. 2005. PMID: 15975090 Free PMC article.
-
The Ubiquitination, Disaggregation and Proteasomal Degradation Machineries in Polyglutamine Disease.Front Mol Neurosci. 2017 Mar 22;10:78. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00078. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28381987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquilin 2 modulates ALS/FTD-linked FUS-RNA complex dynamics and stress granule formation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Dec 4;115(49):E11485-E11494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1811997115. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30442662 Free PMC article.
-
Activated Cdc42-associated kinase 1 is a component of EGF receptor signaling complex and regulates EGF receptor degradation.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Mar;18(3):732-42. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e06-02-0142. Epub 2006 Dec 20. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17182860 Free PMC article.
-
Studies of the role of ubiquitination in the interaction of ubiquilin with the loop and carboxyl terminal regions of presenilin-2.Biochemistry. 2007 Jul 31;46(30):8827-37. doi: 10.1021/bi700604q. Epub 2007 Jul 6. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17614368 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baumeister, W., Walz, J., Zuhl, F., and Seemuller, E. (1998). The proteasome: paradigm of a self-compartmentalizing protease. Cell 92, 367–380. - PubMed
-
- Bedford, F.K., Kittler, J.T., Muller, E., Thomas, P., Uren, J.M., Merlo, D., Wisden, W., Triller, A., Smart, T.G., and Moss, S.J. (2001). GABA(A) receptor cell surface number and subunit stability are regulated by the ubiquitin-like protein Plic-1. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 908–916. - PubMed
-
- Bertolaet, B.L., Clarke, D.J., Wolff, M., Watson, M.H., Henze, M., Divita, G., and Reed, S.I. (2001a). UBA domains mediate protein-protein interactions between two DNA damage-inducible proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 313, 955–963. - PubMed
-
- Bertolaet, B.L., Clarke, D.J., Wolff, M., Watson, M.H., Henze, M., Divita, G., and Reed, S.I. (2001b). UBA domains of DNA damage-inducible proteins interact with ubiquitin. Nat. Struct. Biol. 8, 417–422. - PubMed
-
- Bogyo, M., Shin, S., McMaster, J.S., and Ploegh, H.L. (1998). Substrate binding and sequence preference of the proteasome revealed by active-site-directed affinity probes. Chem. Biol. 5, 307–320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

