Cdk7 is required for full activation of Drosophila heat shock genes and RNA polymerase II phosphorylation in vivo
- PMID: 12972606
- PMCID: PMC193928
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.19.6876-6886.2003
Cdk7 is required for full activation of Drosophila heat shock genes and RNA polymerase II phosphorylation in vivo
Abstract
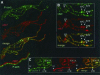
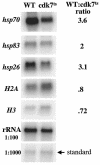
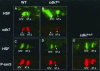
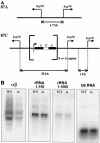
TFIIH has been implicated in several fundamental cellular processes, including DNA repair, cell cycle progression, and transcription. In transcription, the helicase activity of TFIIH functions to melt promoter DNA; however, the in vivo function of the Cdk7 kinase subunit of TFIIH, which has been hypothesized to be involved in RNA polymerase II (Pol II) phosphorylation, is not clearly understood. Using temperature-sensitive and null alleles of cdk7, we have examined the role of Cdk7 in the activation of Drosophila heat shock genes. Several in vivo approaches, including polytene chromosome immunofluorescence, nuclear run-on assays, and, in particular, a protein-DNA cross-linking assay customized for adults, revealed that Cdk7 kinase activity is required for full activation of heat shock genes, promoter-proximal Pol II pausing, and Pol II-dependent chromatin decondensation. The requirement for Cdk7 occurs very early in the transcription cycle. Furthermore, we provide evidence that TFIIH associates with the elongation complex much longer than previously suspected.
Figures

References
-
- Akoulitchev, S., T. P. Makela, R. A. Weinberg, and D. Reinberg. 1995. Requirement for TFIIH kinase activity in transcription by RNA polymerase II. Nature 377:557-560. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl (ed.). 1997. Current protocols in molecular biology. John Wiley & Sons, New York, N.Y.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
