EBNA-1, a bifunctional transcriptional activator
- PMID: 12972608
- PMCID: PMC193932
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.19.6901-6908.2003
EBNA-1, a bifunctional transcriptional activator
Abstract
Transient-transfection assays have been used to identify transcription factors, and genetic analyses of these factors can allow a dissection of their mechanism of activation. Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA-1) has been shown to activate transcription from transfected templates, but its ability to activate transcription from nuclear templates has been controversial. We have established cells with integrated EBNA-1-responsive templates and have shown that EBNA-1 activates transcription from these chromatin-embedded templates dose dependently. A mutational analysis of EBNA-1 has identified a domain required for transcriptional activation of integrated templates, but not of transfected templates. The ability of EBNA-1 to activate transcription from both integrated and transfected templates can be inhibited by a derivative of EBNA-1 lacking the amino acids required for activation from integrated templates. EBNA-1's mode of activating transfected templates is therefore genetically distinct from that acting on integrated templates.
Figures


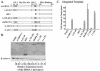
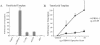
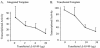
References
-
- Archer, T. K., P. Lefebvre, R. G. Wolford, and G. L. Hager. 1992. Transcription factor loading on the MMTV promoter: a bimodal mechanism for promoter activation. Science 255:1573-1576. (Erratum, 256:161.) - PubMed
-
- Banerjee, S., E. Livanos, and J. M. Vos. 1995. Therapeutic gene delivery in human B-lymphoblastoid cells by engineered non-transforming infectious Epstein-Barr virus. Nat. Med. 1:1303-1308. - PubMed
-
- Calos, M. P. 1996. The potential of extrachromosomal replicating vectors for gene therapy. Trends Genet. 12:463-466. - PubMed
-
- Ceccarelli, D., and L. Frappier. 1998. Separation of the DNA replication and transactivation activities of EBNA-1, the origin binding protein of Epstein-Barr virus. Gene Ther. Mol. Biol. 3:1-10.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
