Functions of the ectodomain and cytoplasmic tyrosine phosphatase domains of receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase Dlar in vivo
- PMID: 12972609
- PMCID: PMC193937
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.19.6909-6921.2003
Functions of the ectodomain and cytoplasmic tyrosine phosphatase domains of receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase Dlar in vivo
Abstract
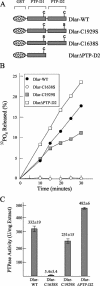
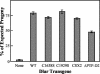
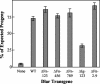
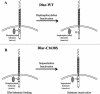
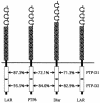
The receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTPase) Dlar has an ectodomain consisting of three immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domains and nine fibronectin type III (FnIII) repeats and a cytoplasmic domain consisting of two PTPase domains, membrane-proximal PTP-D1 and C-terminal PTP-D2. A series of mutant Dlar transgenes were introduced into the Drosophila genome via P-element transformation and were then assayed for their capacity to rescue phenotypes caused by homozygous loss-of-function genotypes. The Ig-like domains, but not the FnIII domains, are essential for survival. Conversely, the FnIII domains, but not the Ig-like domains, are required during oogenesis, suggesting that different domains of the Dlar ectodomain are involved in distinct functions during Drosophila development. All detectable PTPase activity maps to PTP-D1 in vitro. The catalytically inactive mutants of Dlar were able to rescue Dlar(-/-) lethality nearly as efficiently as wild-type Dlar transgenes, while this ability was impaired in the PTP-D2 deletion mutants DlarDeltaPTP-D2 and Dlar(bypass). Dlar-C1929S, in which PTP-D2 has been inactivated, increases the frequency of bypass phenotype observed in Dlar(-/-) genotypes, but only if PTP-D1 is catalytically active in the transgene. These results indicate multiple roles for PTP-D2, perhaps by acting as a docking domain for downstream elements and as a regulator of PTP-D1.
Figures


References
-
- Allard, J. D., R. Herbst, P. M. Carroll, and M. A. Simon. 1998. Mutational analysis of the SRC homology 2 domain protein-tyrosine phosphatase Corkscrew. J. Biol. Chem. 273:13129-13135. - PubMed
-
- Bateman, J., R. S. Reddy, H. Saito, and D. Van Vactor. 2001. The receptor tyrosine phosphatase Dlar and integrins organize actin filaments in the Drosophila follicular epithelium. Curr. Biol. 11:1317-1327. - PubMed
-
- Bateman, J., H. Shu, and D. Van Vactor. 2000. The guanine nucleotide exchange factor trio mediates axonal development in the Drosophila embryo. Neuron 26:93-106. - PubMed
-
- Bilwes, A. M., J. den Hertog, T. Hunter, and J. P. Noel. 1996. Structural basis for inhibition of receptor protein-tyrosine phosphatase-α by dimerization. Nature 382:555-559. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
