Role of Plk2 (Snk) in mouse development and cell proliferation
- PMID: 12972611
- PMCID: PMC193943
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.19.6936-6943.2003
Role of Plk2 (Snk) in mouse development and cell proliferation
Abstract
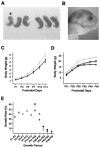
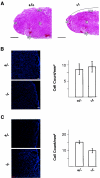
Plk2 (Snk) is a polo-like kinase expressed at G(1) in cultured cells and mainly in the hippocampal neurons in the brains of adult rodents, but its function is poorly understood. We have generated mice deficient in Plk2 by gene targeting. Although Plk2 is not required for postnatal growth, Plk2(-/-) embryos show retarded growth and skeletal development late in gestation. The labyrinthine zone of the placenta is diminished in Plk2(-/-) embryos due to decreased cell proliferation. Cultured Plk2(-/-) embryonic fibroblasts grow more slowly than normal cells and show delayed entry into S phase. These data suggest a role for Plk2 in the cell cycle.
Figures

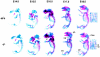
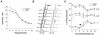
References
-
- Alexandru, G., F. Uhlmann, K. Mechtler, M. A. Poupart, and K. Nasmyth. 2001. Phosphorylation of the cohesin subunit Scc1 by Polo/Cdc5 kinase regulates sister chromatid separation in yeast. Cell 105:459-472. - PubMed
-
- Charron, J., B. A. Malynn, P. Fisher, V. Stewart, L. Jeannotte, S. P. Goff, E. J. Robertson, and F. W. Alt. 1992. Embryonic lethality in mice homozygous for a targeted disruption of the N-myc gene. Genes Dev. 6:2248-2257. - PubMed
-
- Conn, C. W., R. F. Hennigan, W. Dai, Y. Sanchez, and P. J. Stambrook. 2000. Incomplete cytokinesis and induction of apoptosis by overexpression of the mammalian polo-like kinase, Plk3. Cancer Res. 60:6826-6831. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
