A novel human Ada2 homologue functions with Gcn5 or Brg1 to coactivate transcription
- PMID: 12972612
- PMCID: PMC193946
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.19.6944-6957.2003
A novel human Ada2 homologue functions with Gcn5 or Brg1 to coactivate transcription
Abstract
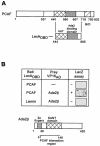
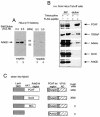
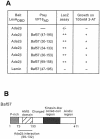
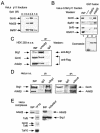
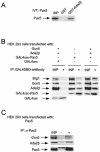
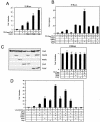
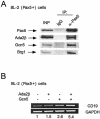
In yeast, the transcriptional adaptor yeast Ada2 (yAda2) is a part of the multicomponent SAGA complex, which possesses histone acetyltransferase activity through action of the yGcn5 catalytic enzyme. yAda2, among several SAGA proteins, serves to recruit SAGA to genes via interactions with promoter-bound transcription factors. Here we report identification of a new human Ada2 homologue, hAda2beta. Ada2beta differs both biochemically and functionally from the previously characterized hAda2alpha, which is a stable component of the human PCAF (human Gcn5 homologue) acetylase complex. Ada2beta, relative to Ada2alpha, interacted selectively, although not stably, with the Gcn5-containing histone acetylation complex TFTC/STAGA. In addition, Ada2beta interacted with Baf57 (a component of the human Swi/Snf complex) in a yeast two-hybrid screen and associated with human Swi/Snf in vitro. In functional assays, hAda2beta (but not Ada2alpha), working in concert with Gcn5 (but not PCAF) or Brg1 (the catalytic component of hSwi/Snf complex), increased transcription via the B-cell-specific transcription factor Pax5/BSAP. These findings support the view that Gcn5 and PCAF have distinct roles in vivo and suggest a new mechanism of coactivator function, in which a single adaptor protein (Ada2beta) can coordinate targeting of both histone acetylation and chromatin remodeling activities.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A human SPT3-TAFII31-GCN5-L acetylase complex distinct from transcription factor IID.J Biol Chem. 1998 Sep 11;273(37):23781-5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.37.23781. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9726987
-
Human STAGA complex is a chromatin-acetylating transcription coactivator that interacts with pre-mRNA splicing and DNA damage-binding factors in vivo.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Oct;21(20):6782-95. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.20.6782-6795.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11564863 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of human proteins functionally conserved with the yeast putative adaptors ADA2 and GCN5.Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Feb;16(2):593-602. doi: 10.1128/MCB.16.2.593. Mol Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8552087 Free PMC article.
-
Recruitment of chromatin remodelling factors during gene activation via the glucocorticoid receptor N-terminal domain.Biochem Soc Trans. 2000;28(4):410-4. Biochem Soc Trans. 2000. PMID: 10961930 Review.
-
Distinct GCN5/PCAF-containing complexes function as co-activators and are involved in transcription factor and global histone acetylation.Oncogene. 2007 Aug 13;26(37):5341-57. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210604. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 17694077 Review.
Cited by
-
Plasmodium falciparum histone acetyltransferase, a yeast GCN5 homologue involved in chromatin remodeling.Eukaryot Cell. 2004 Apr;3(2):264-76. doi: 10.1128/EC.3.2.264-276.2004. Eukaryot Cell. 2004. PMID: 15075257 Free PMC article.
-
EBF1 drives hallmark B cell gene expression by enabling the interaction of PAX5 with the MLL H3K4 methyltransferase complex.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 15;11(1):1537. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-81000-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33452395 Free PMC article.
-
Pax5 and linker histone H1 coordinate DNA methylation and histone modifications in the 3' regulatory region of the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Oct;28(19):6123-33. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00233-08. Epub 2008 Jul 21. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18644860 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of SAGA in development and disease.Epigenomics. 2014 Jun;6(3):329-39. doi: 10.2217/epi.14.22. Epigenomics. 2014. PMID: 25111486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of transcription complexes that contain the double bromodomain protein Brd2 and chromatin remodeling machines.J Proteome Res. 2006 Mar;5(3):502-11. doi: 10.1021/pr050430u. J Proteome Res. 2006. PMID: 16512664 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aasland, R., A. F. Stewart, and T. Gibson. 1996. The SANT domain: a putative DNA-binding domain in the SWI-SNF and ADA complexes, the transcriptional co-repressor N-CoR and TFIIIB. Trends Biochem. Sci. 21:87-88. - PubMed
-
- Barlev, N. A., R. Candau, L. Wang, P. Darpino, N. Silverman, and S. L. Berger. 1995. Characterization of physical interactions of the putative transcriptional adaptor, ADA2, with acidic activation domains and TATA-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 270:19337-19344. - PubMed
-
- Barlev, N. A., L. Liu, N. H. Chehab, K. Mansfield, K. G. Harris, T. D. Halazonetis, and S. L. Berger. 2001. Acetylation of p53 activates transcription through recruitment of coactivators/histone acetyltransferases. Mol. Cell 8:1243-1254. - PubMed
-
- Bell, B., E. Scheer, and L. Tora. 2001. Identification of hTAF(II)80 delta links apoptotic signaling pathways to transcription factor TFIID function. Mol. Cell 8:591-600. - PubMed
-
- Bell, B., and L. Tora. 1999. Regulation of gene expression by multiple forms of TFIID and other novel TAFII-containing complexes. Exp. Cell Res. 246:11-19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
