The STT3a subunit isoform of the Arabidopsis oligosaccharyltransferase controls adaptive responses to salt/osmotic stress
- PMID: 12972670
- PMCID: PMC197294
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.013862
The STT3a subunit isoform of the Arabidopsis oligosaccharyltransferase controls adaptive responses to salt/osmotic stress
Abstract
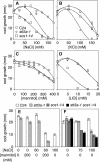
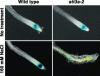
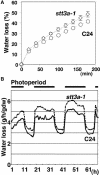
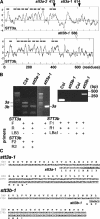
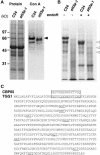
Arabidopsis stt3a-1 and stt3a-2 mutations cause NaCl/osmotic sensitivity that is characterized by reduced cell division in the root meristem. Sequence comparison of the STT3a gene identified a yeast ortholog, STT3, which encodes an essential subunit of the oligosaccharyltransferase complex that is involved in protein N-glycosylation. NaCl induces the unfolded protein response in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and cell cycle arrest in root tip cells of stt3a seedlings, as determined by expression profiling of ER stress-responsive chaperone (BiP-GUS) and cell division (CycB1;1-GUS) genes, respectively. Together, these results indicate that plant salt stress adaptation involves ER stress signal regulation of cell cycle progression. Interestingly, a mutation (stt3b-1) in another Arabidopsis STT3 isogene (STT3b) does not cause NaCl sensitivity. However, the stt3a-1 stt3b-1 double mutation is gametophytic lethal. Apparently, STT3a and STT3b have overlapping and essential functions in plant growth and developmental processes, but the pivotal and specific protein glycosylation that is a necessary for recovery from the unfolded protein response and for cell cycle progression during salt/osmotic stress recovery is associated uniquely with the function of the STT3a isoform.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Construction of green fluorescence protein mutant to monitor STT3B-dependent N-glycosylation.FEBS J. 2018 Mar;285(5):915-928. doi: 10.1111/febs.14375. Epub 2018 Jan 11. FEBS J. 2018. PMID: 29282902
-
[Characterization of the functional domain of STT3a of oligosaccharyltransferase from Dunaliella salina].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2010 Jun;26(6):760-6. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2010. PMID: 20815255 Chinese.
-
OST4 is a subunit of the mammalian oligosaccharyltransferase required for efficient N-glycosylation.J Cell Sci. 2013 Jun 15;126(Pt 12):2595-606. doi: 10.1242/jcs.115410. Epub 2013 Apr 19. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23606741 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Insight into the Mechanism of N-Linked Glycosylation by Oligosaccharyltransferase.Biomolecules. 2020 Apr 17;10(4):624. doi: 10.3390/biom10040624. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32316603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cotranslational and posttranslocational N-glycosylation of proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015 May;41:71-8. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.11.005. Epub 2014 Nov 24. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 25460543 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The UDP-glucose: glycoprotein glucosyltransferase (UGGT), a key enzyme in ER quality control, plays a significant role in plant growth as well as biotic and abiotic stress in Arabidopsis thaliana.BMC Plant Biol. 2015 May 28;15:127. doi: 10.1186/s12870-015-0525-2. BMC Plant Biol. 2015. PMID: 26017403 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of differentially expressed transcripts in the gills of freshwater prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii) under salt stress.ScientificWorldJournal. 2012;2012:149361. doi: 10.1100/2012/149361. Epub 2012 Apr 19. ScientificWorldJournal. 2012. PMID: 22619594 Free PMC article.
-
Interference of Arabidopsis N-Acetylglucosamine-1-P Uridylyltransferase Expression Impairs Protein N-Glycosylation and Induces ABA-Mediated Salt Sensitivity During Seed Germination and Early Seedling Development.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jun 7;13:903272. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.903272. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35747876 Free PMC article.
-
HOS3, an ELO-like gene, inhibits effects of ABA and implicates a S-1-P/ceramide control system for abiotic stress responses in Arabidopsis thaliana.Mol Plant. 2009 Jan;2(1):138-51. doi: 10.1093/mp/ssn085. Mol Plant. 2009. PMID: 19529829 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-targeted trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase I harbors a novel peroxisomal targeting signal 1 and is essential for flowering and development.Planta. 2020 Apr 18;251(5):98. doi: 10.1007/s00425-020-03389-z. Planta. 2020. PMID: 32306103 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnold, E., and Tanner, W. (1982). An obligatory role of protein glycosylation in the life cycle of yeast cells. FEBS Lett. 148, 49–53. - PubMed
-
- Benton, B.K., Plump, S.D., Roos, J., Lennarz, W.J., and Cross, F.R. (1996). Over-expression of S. cerevisiae G1 cyclins restores the viability of alg1 N-glycosylation mutants. Curr. Genet. 29, 106–113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

