Specific and common antigens of Clonorchis sinensis and Opisthorchis viverrini(Opisthorchidae, Trematoda)
- PMID: 12972729
- PMCID: PMC2717500
- DOI: 10.3347/kjp.2003.41.3.155
Specific and common antigens of Clonorchis sinensis and Opisthorchis viverrini(Opisthorchidae, Trematoda)
Abstract
The antigenic characterizations and serological reactions of human liver flukes, Clonorchis sinensis and Opisthorchis viverrini, were analyzed by immunoblot. The antigenic profiles of the crude extract of Clonorchis contained major proteins of 8, 26-28, 34-37, 43, and 70 kDa, and those of Opisthorchis 34-37, 43, 70, and 100 kDa. Of these, the 8, 26-28 and 34-37 kDa bands of Clonorchis and the 100 kDa of Opisthorchis were major components of each excretory-secretory antigen. The 8 and 26-28 kDa bands were specific to Clonorchis but the 100 kDa of Opisthorchis cross-reacted with the sera of clonorchiasis, and the 34-37, 70 and 100 kDa bands cross-reacted with sera of other helminthiases. The frequency and intensity of the immunoblot reactions were positively correlated with the intensity of the liver fluke infection.
Figures
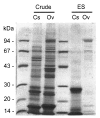
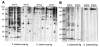
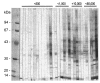

References
-
- Chen M, Lu Y, Hua X, Mott KE. Progress in assessment of morbidity due to Clonorchis sinensis infection: a review of recent literature. Trop Dis Bull. 1994;91:R9–R65.
-
- Elkins DB, Sithithaworn P, Haswell-Elkins M, Kaewkes S, Awacharagan P, Wongratanacheewin S. Opisthorchis viverrini: relationships between egg counts, worms recovered and antibody levels within an endemic community in northeast Thailand. Parasitology. 1991;102 Pt 2:283–288. - PubMed
-
- Garcia LS, Bruckner DA. Diagnostic Medical Parasitology. 3rd ed. Washington, D.C., USA: ASM Press; 1997.
-
- Haswell-Elkins MR, Satarug S, Elkins DB. Opisthorchis viverrini infection in northeast Thailand and its relationship to cholangiocarcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1992;7:538–548. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

