Matrix metalloproteinases production in malignant pleural effusions after talc pleurodesis
- PMID: 12974766
- PMCID: PMC1808842
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2003.02262.x
Matrix metalloproteinases production in malignant pleural effusions after talc pleurodesis
Abstract
In this study we have evaluated the modifications of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in malignant pleural fluids taken from patients suffering from lung cancer and treated with intrapleural talc instillation to induce pleurodesis. Furthermore, we have analysed the variations of some inflammatory mediators (C-reactive protein, alpha-1 antitrypsin) and of a protein (plasminogen) involved in MMP activation. In all patients the clinical improvement after talc pleurodesis was followed by a reduction in MMP-1, TIMP-1, C-reactive protein, alpha-1 antitrypsin and plasminogen activity. Furthermore, MMP-9 levels were variable; in fact, in some patients they were high at the beginning of treatment, in others they increased a few days after pleurodesis induction. These inhibitory effects of talc on MMP-1 and inflammatory mediators associated with the reduction of pleural effusion could constitute an effective means to evaluate the evolution of the treatment.
Figures
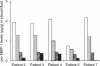
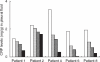
Similar articles
-
[The thoracoscopic talc pleurodesis with intraoperative pleural biopsy - a retrospective analysis in patients with malignant pleural effusion].Zentralbl Chir. 2010 Feb;135(1):54-8. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1224646. Epub 2009 Dec 22. Zentralbl Chir. 2010. PMID: 20029741 German.
-
Failure of talc pleurodesis is associated with increased pleural fibrinolysis.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995 Mar;151(3 Pt 1):785-90. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/151.3_Pt_1.785. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995. PMID: 7881671
-
[Treatment of malignant pleural effusion by pleurodesis with talc].Chir Ital. 2000 Sep-Oct;52(5):541-7. Chir Ital. 2000. PMID: 11190547 Italian.
-
Management of malignant pleural effusions.Respirology. 2004 Jun;9(2):148-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1843.2004.00566.x. Respirology. 2004. PMID: 15182263 Review.
-
Pleurodesis for malignant pleural effusions: current controversies and variations in practices.Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2004 Jul;10(4):305-10. doi: 10.1097/01.mcp.0000129756.87090.55. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2004. PMID: 15220757 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemical pleurodesis - a review of mechanisms involved in pleural space obliteration.Respir Res. 2019 Nov 7;20(1):247. doi: 10.1186/s12931-019-1204-x. Respir Res. 2019. PMID: 31699094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Profile of Metalloproteinases and Their Association with Inflammatory Markers in Pleural Effusions.Lung. 2016 Dec;194(6):1021-1027. doi: 10.1007/s00408-016-9945-5. Epub 2016 Sep 27. Lung. 2016. PMID: 27677622
References
-
- Prevost A, Costa B, Elamarti R, et al. Long-term effect and tolerance of talc slurry for control of malignant pleural effusions. Oncol Rep. 2001;8:1327–31. - PubMed
-
- Mager HJ, Maesen B, Verzijlbergen F, Schramel F. Distribution of talc suspension during treatment of malignant pleural effusion with talc pleurodesis. Lung Cancer. 2002;36:77–81. - PubMed
-
- Cheng DS, Rogers J, Wheeler A, Parker R, Teixeira L, Light RW. The effects of intrapleural polyclonal anti-tumor factor alpha (TNF alpha) Fab fragments on pleurodesis in rabbits. Lung. 2000;178:19–29. - PubMed
-
- Lee YC, Lane KB. The many faces of transforming growth factor-beta in pleural diseases. Opin Pulm Med. 2001;7:173–9. - PubMed
-
- Hack CE, Wolbink GJ, Schalkwijk C, Speijer H, Hermens WT, van den Bosch H. A role for secretory phospholipase A2 and C-reactive protein in the removal of injured cells. Immunol Today. 1997;18:111–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

