Bench-to-bedside review: microvascular dysfunction in sepsis--hemodynamics, oxygen transport, and nitric oxide
- PMID: 12974969
- PMCID: PMC270719
- DOI: 10.1186/cc2353
Bench-to-bedside review: microvascular dysfunction in sepsis--hemodynamics, oxygen transport, and nitric oxide
Abstract
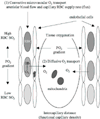
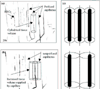
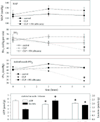
The microcirculation is a complex and integrated system that supplies and distributes oxygen throughout the tissues. The red blood cell (RBC) facilitates convective oxygen transport via co-operative binding with hemoglobin. In the microcirculation oxygen diffuses from the RBC into neighboring tissues, where it is consumed by mitochondria. Evidence suggests that the RBC acts as deliverer of oxygen and 'sensor' of local oxygen gradients. Within vascular beds RBCs are distributed actively by arteriolar tone and passively by rheologic factors, including vessel geometry and RBC deformability. Microvascular oxygen transport is determined by microvascular geometry, hemodynamics, and RBC hemoglobin oxygen saturation. Sepsis causes abnormal microvascular oxygen transport as significant numbers of capillaries stop flowing and the microcirculation fails to compensate for decreased functional capillary density. The resulting maldistribution of RBC flow results in a mismatch of oxygen delivery with oxygen demand that affects both critical oxygen delivery and oxygen extraction ratio. Nitric oxide (NO) maintains microvascular homeostasis by regulating arteriolar tone, RBC deformability, leukocyte and platelet adhesion to endothelial cells, and blood volume. NO also regulates mitochondrial respiration. During sepsis, NO over-production mediates systemic hypotension and microvascular reactivity, and is seemingly protective of microvascular blood flow.
Figures




References
-
- Gilbert RP. Mechanisms of the hemodynamic effects of endotoxin. Physiol Rev. 1960;40:245–278. - PubMed
-
- Carroll GC, Snyder JV. Hyperdynamic severe intravascular sepsis depends on fluid administration in cynomolgus monkey. Am J Physiol. 1982;243:R131–R141. - PubMed
-
- Krishnagopalan S, Kumar A, Parrillo JE, Kumar A. Myocardial dysfunction in the patient with sepsis. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2002;8:376–388. - PubMed
-
- Zhang H, Rogiers P, Smail N, Cabral A, Preiser JC, Peny MO, Vincent JL. Effects of nitric oxide on blood flow distribution and O2 extraction capabilities during endotoxic shock. J Appl Physiol. 1997;83:1164–1173. - PubMed
-
- Yang S, Cioffi WG, Bland KI, Chaudry IH, Wang P. Differential alterations in systemic and regional oxygen delivery and consumption during the early and late stages of sepsis. J Trauma. 1999;47:706–712. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

