Synoviolin/Hrd1, an E3 ubiquitin ligase, as a novel pathogenic factor for arthropathy
- PMID: 12975321
- PMCID: PMC218080
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1096603
Synoviolin/Hrd1, an E3 ubiquitin ligase, as a novel pathogenic factor for arthropathy
Abstract
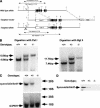
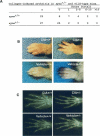
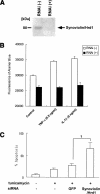
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is one of the most critical articular diseases with synovial hyperplasia followed by impairment of quality of life. However, the mechanism(s) that regulates synovial cell outgrowth is not fully understood. To clarify its mechanism(s), we carried out immunoscreening by using antirheumatoid synovial cell antibody and identified and cloned "Synoviolin/Hrd1", an E3 ubiquitin ligase. Synoviolin/Hrd1 was highly expressed in the rheumatoid synovium, and mice overexpressing this enzyme developed spontaneous arthropathy. Conversely, synoviolin/hrd1(+/-) mice were resistant to collagen-induced arthritis by enhanced apoptosis of synovial cells. We conclude that Synoviolin/Hrd1 is a novel causative factor for arthropathy by triggering synovial cell outgrowth through its antiapoptotic effects. Our findings provide a new pathogenetic model of RA and suggest that Synoviolin/Hrd1 could be targeted as a therapeutic strategy for RA.
Figures







References
-
- Aono H., Fujisawa, K., Hasunuma, T., Marriott, S.J., and Nishioka, K. 1998. Extracellular human T cell leukemia virus type I tax protein stimulates the proliferation of human synovial cells. Arthritis Rheum. 41: 1995-2003. - PubMed
-
- Arend W.P. 2001. Physiology of cytokine pathways in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 45: 101-106. - PubMed
-
- Bays N.W., Gardner, R.G., Seelig, L.P., Joazeiro, C.A., and Hampton, R.Y. 2001. Hrd1p/Der3p is a membrane-anchored ubiquitin ligase required for ER-associated degradation. Nat. Cell Biol. 3: 24-29. - PubMed
-
- Bence N.F., Sampat, R.M., and Kopito, R.R. 2001. Impairment of the ubiquitin-proteasome system by protein aggregation. Science 292: 1552-1555. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
