Coupled degradation of a small regulatory RNA and its mRNA targets in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 12975324
- PMCID: PMC218075
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1127103
Coupled degradation of a small regulatory RNA and its mRNA targets in Escherichia coli
Abstract
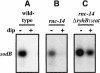
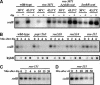
RyhB is a small antisense regulatory RNA that is repressed by the Fur repressor and negatively regulates at least six mRNAs encoding Fe-binding or Fe-storage proteins in Escherichia coli. When Fe is limiting, RyhB levels rise, and target mRNAs are rapidly degraded. RyhB is very stable when measured after treatment of cells with the transcription inhibitor rifampicin, but is unstable when overall mRNA transcription continues. We propose that RyhB turnover is coupled to and dependent on pairing with the target mRNAs. Degradation of both mRNA targets and RyhB is dependent on RNase E and is slowed in degradosome mutants. RyhB requires the RNA chaperone Hfq. In the absence of Hfq, RyhB is unstable, even when general transcription is inhibited; degradation is dependent upon RNase E. Hfq and RNase E bind similar sites on the RNA; pairing may allow loss of Hfq and access by RNase E. Two other Hfq-dependent small RNAs, DsrA and OxyS, are also stable when overall transcription is off, and unstable when it is not, suggesting that they, too, are degraded when their target mRNAs are available for pairing. Thus, this large class of regulatory RNAs share an unexpected intrinsic mechanism for shutting off their action.
Figures





Comment in
-
Degradation of targeted mRNAs in Escherichia coli: regulation by a small antisense RNA.Genes Dev. 2003 Oct 1;17(19):2351-5. doi: 10.1101/gad.1147003. Genes Dev. 2003. PMID: 14522943 Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Aiba H., Adhya, S., and de Crombrugghe, B. 1981. Evidence for two functional gal promoters in intact Escherichia coli cells. J. Biol. Chem. 256: 11905-11910. - PubMed
-
- Altuvia S., Weinstein-Fischer, D., Zhang, A., Postow, L., and Storz, G. 1997. A small stable RNA induced by oxidative stress: Role as a pleiotropic regulator and antimutator. Cell 90: 43-53. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. 2001. microRNAs: Tiny regulators with great potential. Cell 107: 823-826. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
