The budding yeast silencing protein Sir1 is a functional component of centromeric chromatin
- PMID: 12975325
- PMCID: PMC218072
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1131103
The budding yeast silencing protein Sir1 is a functional component of centromeric chromatin
Abstract
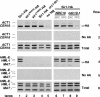
In fission yeast and multicellular organisms, centromere-proximal regions of chromosomes are heterochromatic, containing proteins that silence gene expression. In contrast, the relationship between heterochromatin proteins and kinetochore function in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae remains largely unexplored. Here we report that the yeast heterochromatin protein Sir1 is a component of centromeric chromatin and contributes to mitotic chromosome stability. Sir1 recruitment to centromeres occurred through a novel mechanism independent of its interaction with the origin recognition complex (ORC). Sir1 function at centromeres was distinct from its role in forming heterochromatin, because the Sir2-4 proteins were not associated with centromeric regions. Sir1 bound to Cac1, a subunit of chromatin assembly factor I (CAF-I), and helped to retain Cac1 at centromeric loci. These studies reveal that although budding yeast and mammalian cells use fundamentally different mechanisms of forming heterochromatin, they both use silencing proteins to attract the histone deposition factor CAF-I to centromeric chromatin.
Figures

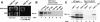

Similar articles
-
Chromatin assembly: the kinetochore connection.Curr Biol. 2002 Apr 2;12(7):R256-8. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)00786-8. Curr Biol. 2002. PMID: 11937044 Review.
-
Functional roles for evolutionarily conserved Spt4p at centromeres and heterochromatin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.EMBO J. 2004 Apr 21;23(8):1804-14. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600161. Epub 2004 Apr 1. EMBO J. 2004. PMID: 15057281 Free PMC article.
-
The yeast RSC chromatin-remodeling complex is required for kinetochore function in chromosome segregation.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 May;23(9):3202-15. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.9.3202-3215.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12697820 Free PMC article.
-
Heterochromatin and RNAi regulate centromeres by protecting CENP-A from ubiquitin-mediated degradation.PLoS Genet. 2018 Aug 8;14(8):e1007572. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007572. eCollection 2018 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 30089114 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into assembly and regulation of centromeric chromatin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jul;1819(7):776-83. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.02.008. Epub 2012 Feb 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22366340 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Ku complex in silencing the cryptic mating-type loci of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2008 Oct;180(2):771-83. doi: 10.1534/genetics.108.091710. Epub 2008 Aug 20. Genetics. 2008. PMID: 18716325 Free PMC article.
-
The role of SIRT3 in homeostasis and cellular health.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Aug 2;18:1434459. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1434459. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39157755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural basis for origin recognition complex 1 protein-silence information regulator 1 protein interaction in epigenetic silencing.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Jun 14;102(24):8519-24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0502946102. Epub 2005 Jun 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15937111 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of histone deposition proteins Asf1/Hir1 by multiple DNA damage checkpoint kinases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2005 Nov;171(3):885-99. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.044719. Epub 2005 Jul 14. Genetics. 2005. PMID: 16020781 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin assembly factor-1 preserves genome stability in ctf4Δ cells by promoting sister chromatid cohesion.Cell Stress. 2023 Aug 14;7(9):69-89. doi: 10.15698/cst2023.09.289. eCollection 2023 Sep 11. Cell Stress. 2023. PMID: 37662646 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bernard P., Maura, J.F., Partridge, J.F., Genier, S., Javerzat, J.P., and Allshire, R.C. 2001. Requirement of heterochromatin for cohesion at centromeres. Science 294: 2539-2542. - PubMed
-
- Biggins S. and Walczak, C.E. 2003. Captivating capture: How microtubules attach to kinetochores. Curr. Biol. 13: R449-R460. - PubMed
-
- Bryk M., Briggs, S.D., Strahl, B.D., Curcio, M.J., Allis, C.D., and Winston, F. 2002. Evidence that Set1, a factor required for methylation of histone H3, regulates rDNA silencing in S. cerevisiae by a Sir2-independent mechanism. Curr. Biol. 12: 165-170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
