Site-specific inductive and inhibitory activities of MMP-2 and MMP-3 orchestrate mammary gland branching morphogenesis
- PMID: 12975354
- PMCID: PMC2172848
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200302090
Site-specific inductive and inhibitory activities of MMP-2 and MMP-3 orchestrate mammary gland branching morphogenesis
Abstract
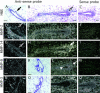
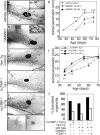
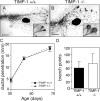
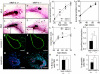
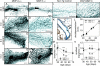
During puberty, mouse mammary epithelial ducts invade the stromal mammary fat pad in a wave of branching morphogenesis to form a complex ductal tree. Using pharmacologic and genetic approaches, we find that mammary gland branching morphogenesis requires transient matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) activity for invasion and branch point selection. MMP-2, but not MMP-9, facilitates terminal end bud invasion by inhibiting epithelial cell apoptosis at the start of puberty. Unexpectedly, MMP-2 also represses precocious lateral branching during mid-puberty. In contrast, MMP-3 induces secondary and tertiary lateral branching of ducts during mid-puberty and early pregnancy. Nevertheless, the mammary gland is able to develop lactational competence in MMP mutant mice. Thus, specific MMPs refine the mammary branching pattern by distinct mechanisms during mammary gland branching morphogenesis.
Figures
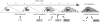
References
-
- Affolter, M., S. Bellusci, N. Itoh, B. Shilo, J.P. Thiery, and Z. Werb. 2003. Tube or not tube: remodeling epithelial tissues by branching morphogenesis. Dev. Cell. 4:11–18. - PubMed
-
- Baker, A.H., D.R. Edwards, and G. Murphy. 2002. Metalloproteinase inhibitors: biological actions and therapeutic opportunities. J. Cell Sci. 115:3719–3727. - PubMed
-
- Blatchford, D.R., L.H. Quarrie, E. Tonner, C. McCarthy, D.J. Flint, and C.J. Wilde. 1999. Influence of microenvironment on mammary epithelial cell survival in primary culture. J. Cell. Physiol. 181:304–311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

