CD4+CD25+ T cells regulate virus-specific primary and memory CD8+ T cell responses
- PMID: 12975455
- PMCID: PMC2194203
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20030171
CD4+CD25+ T cells regulate virus-specific primary and memory CD8+ T cell responses
Abstract
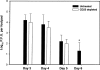
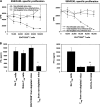
Naturally occurring CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells appear important to prevent activation of autoreactive T cells. This article demonstrates that the magnitude of a CD8+ T cell-mediated immune response to an acute viral infection is also subject to control by CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells (Treg). Accordingly, if natural Treg were depleted with specific anti-CD25 antibody before infection with HSV, the resultant CD8+ T cell response to the immunodominant peptide SSIEFARL was significantly enhanced. This was shown by several in vitro measures of CD8+ T cell reactivity and by assays that directly determine CD8+ T cell function, such as proliferation and cytotoxicity in vivo. The enhanced responsiveness in CD25-depleted animals was between three- and fourfold with the effect evident both in the acute and memory phases of the immune response. Surprisingly, HSV infection resulted in enhanced Treg function with such cells able to suppress CD8+ T cell responses to both viral and unrelated antigens. Our results are discussed both in term of how viral infection might temporarily diminish immunity to other infectious agents and their application to vaccines. Thus, controlling suppressor effects at the time of vaccination could result in more effective immunity.
Figures











References
-
- Sakaguchi, S., N. Sakaguchi, M. Asano, M. Itoh, and M. Toda. 1995. Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune diseases. J. Immunol. 155:1151–1164. - PubMed
-
- Suri-Payer, E., A.Z. Amar, A.M. Thornton, and E.M. Shevach. 1998. CD4+CD25+ T cells inhibit both the induction and effector function of autoreactive T cells and represent a unique lineage of immunoregulatory cells. J. Immunol. 160:1212–1218. - PubMed
-
- McHugh, R.S., E.M. Shevach, and A.M. Thornton. 2001. Control of organ-specific autoimmunity by immunoregulatory CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells. Microbes Infect. 3:919–927. - PubMed
-
- Hori, S., T.L. Carvalho, and J. Demengeot. 2002. CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells suppress CD4+ T cell-mediated pulmonary hyperinflammation driven by Pneumocystis carinii in immunodeficient mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 32:1282–1291. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

