Characterization of the CD4+ T cell response to Epstein-Barr virus during primary and persistent infection
- PMID: 12975456
- PMCID: PMC2194204
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20022058
Characterization of the CD4+ T cell response to Epstein-Barr virus during primary and persistent infection
Abstract
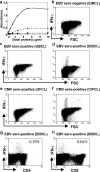
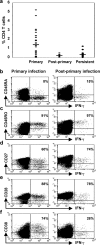
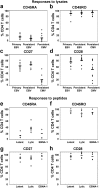
The CD8+ T cell response to Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is well characterized. Much less is known about the evolution of the CD4+ T cell response. Here we show that EBV stimulates a primary burst of effector CD4+ T cells and this is followed by a period of down-regulation. A small population of EBV-specific effector CD4+ T cells survives during the lifelong persistent phase of infection. The EBV-specific effector CD4+ T cells accumulate within a CD27+ CD28+ differentiation compartment during primary infection and remain enriched within this compartment throughout the persistent phase of infection. Analysis of CD4+ T cell responses to individual epitopes from EBV latent and lytic cycle proteins confirms the observation that the majority of the effector cells express both CD27 and CD28, although CD4+ T cells specific for lytic cycle antigens have a greater tendency to express CD45RA than those specific for the latent antigens. In clear contrast, effector CD4+ T cells specific for cytomegalovirus (CMV) accumulate within the CD27- CD28+ and CD27- CD28- compartments. There are striking parallels in terms of the differentiation of CD8+ T cells specific for EBV and CMV. The results challenge current ideas on the definition of memory subsets.
Figures


References
-
- Hintzen, R.Q., R. de Jong, S.M.A. Lens, M. Brouwer, P. Baars, and R.A.W. van Lier. 1993. Regulation of CD27 expression on subsets of mature T lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 151:2426–2435. - PubMed
-
- Azuma, M., J.H. Phillips, and L.L. Lanier. 1993. CD28− T lymphocytes – antigenic and functional properties. J. Immunol. 150:1147–1159. - PubMed
-
- Hamann, D., S. Kostense, K.C. Wolthers, S.A. Otto, P.A. Baars, F. Miedema, and R.A. van Lier. 1999. Evidence that human CD8+CD45RA+CD27− cells are induced by antigen and evolve through extensive rounds of division. Int. Immunol. 11:1027–1033. - PubMed
-
- Posnett, D.N., J.W. Edinger, J.S. Manavalan, C. Irwin, and G. Marodon. 1999. Differentiation of human CD8+ T cells: implications for in vivo persistence of CD8+ CD28− cytotoxic effector clones. Int. Immunol. 11:229–241. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

