Long QT syndrome: novel insights into the mechanisms of cardiac arrhythmias
- PMID: 12975462
- PMCID: PMC193679
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI19844
Long QT syndrome: novel insights into the mechanisms of cardiac arrhythmias
Abstract
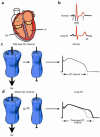
The congenital long QT syndrome is a rare disorder in which mutation carriers are at risk for polymorphic ventricular tachycardia and/or sudden cardiac death. Discovery and analysis of gene mutations associated with variants of this disorder have provided novel insight into mechanisms of cardiac arrhythmia and have raised the possibility of mutation-specific therapeutic intervention.
Figures
References
-
- Jervell A, Lange-Nielsen F. Congential deafmutism, functional heart disease with prolongation of the Q interval, and sudden death. Am. Heart J. 1957;54:59–68. - PubMed
-
- Levine SA, Woodworth CR. Congenital deaf-mutism, prolonged Q-T interval, syncopal attacks and sudden death. N. Engl. J. Med. 1958;259:412–417. - PubMed
-
- Romano C, Gemme G, Pongiglione R. Artimie cardiache rare dell’eta pediatria. Clin. Pediatr. (Phila.). 1963;45:656–683. - PubMed
-
- Ward OC. New familial cardiac syndrome in children. J. Ir. Med. Assoc. 1964;54:103–106. - PubMed
-
- Moss AJ, Schwartz PJ. Delayed repolarization (QT or QTU prolongation) and malignant ventricular arrhythmias. Mod. Concepts Cardiovasc. Dis. 1982;51:85–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

