Chronic stress and obesity: a new view of "comfort food"
- PMID: 12975524
- PMCID: PMC208820
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1934666100
Chronic stress and obesity: a new view of "comfort food"
Abstract
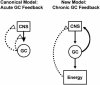
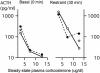
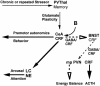
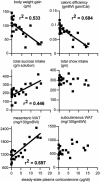
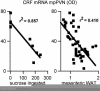
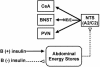
The effects of adrenal corticosteroids on subsequent adrenocorticotropin secretion are complex. Acutely (within hours), glucocorticoids (GCs) directly inhibit further activity in the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis, but the chronic actions (across days) of these steroids on brain are directly excitatory. Chronically high concentrations of GCs act in three ways that are functionally congruent. (i) GCs increase the expression of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) mRNA in the central nucleus of the amygdala, a critical node in the emotional brain. CRF enables recruitment of a chronic stress-response network. (ii) GCs increase the salience of pleasurable or compulsive activities (ingesting sucrose, fat, and drugs, or wheel-running). This motivates ingestion of "comfort food." (iii) GCs act systemically to increase abdominal fat depots. This allows an increased signal of abdominal energy stores to inhibit catecholamines in the brainstem and CRF expression in hypothalamic neurons regulating adrenocorticotropin. Chronic stress, together with high GC concentrations, usually decreases body weight gain in rats; by contrast, in stressed or depressed humans chronic stress induces either increased comfort food intake and body weight gain or decreased intake and body weight loss. Comfort food ingestion that produces abdominal obesity, decreases CRF mRNA in the hypothalamus of rats. Depressed people who overeat have decreased cerebrospinal CRF, catecholamine concentrations, and hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal activity. We propose that people eat comfort food in an attempt to reduce the activity in the chronic stress-response network with its attendant anxiety. These mechanisms, determined in rats, may explain some of the epidemic of obesity occurring in our society.
Figures

References
-
- Keller-Wood, M. E. & Dallman, M. F. (1984) Endocr. Rev. 5, 1–24. - PubMed
-
- Buwalda, B., De Boer, S. F., Schmidt, E. D., Felszeghy, K., Nyaka, C., Sgoigo, A., Van der Begt, B. J., Tilders, F. H. J., Bohus, B. & Koolhaas, J. M. (1999) J. Neuroendocrinol. 11, 512–520. - PubMed
-
- Akana, S. F. & Dallman, M. F. (1997) Endocrinology 138, 3249–3258. - PubMed
-
- Young, E. A., Kwak, S. P. & Kottak, J. (1995) J. Neuroendocrinol. 7, 37–45. - PubMed
-
- Kuipers, S. D., Trentani, A., den Boer, J. A. & Ter Horst, G. J. (2003) J. Neurochem. 85, 1312–1323. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

