Effects of buthionine sulfoximine treatment on cellular glutathione levels and cytotoxicities of cisplatin, carboplatin and radiation in human stomach and ovarian cancer cell lines
- PMID: 1306072
- PMCID: PMC4532113
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.1992.7.2.111
Effects of buthionine sulfoximine treatment on cellular glutathione levels and cytotoxicities of cisplatin, carboplatin and radiation in human stomach and ovarian cancer cell lines
Abstract
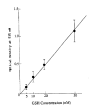
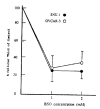
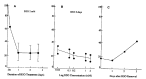
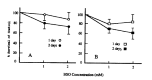
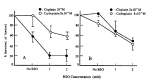
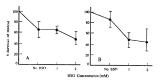
Chemotherapy failure remains a significant medical problem in the treatment of neoplastic disease and is thought to be due to many different factors including membrane transport, p-glycoprotein in multidrug resistance, glutathione and its related enzymes, topoisomerase II and DNA repair. Glutathione is a major constituent of non-protein thiol and participates in detoxification of chemotherapy and radiation. Thus, glutathione concentration is correlated with sensitivity to alkylating agents and radiation, and increased in resistant cell lines. Buthionine sulfoximine (BSO) is an inhibitor of glutathione biosynthesis and may increase cytotoxicities of alkylating agents, including melphalan and cisplatin, and radiation in sensitive and resistant cell lines. We studied effects on cellular glutathione levels and cytotoxicities of cisplatin, carboplatin and radiation by BSO treatment in human stomach cancer cell line (SNU-1) and ovarian cancer cell line (OVCAR-3). The results were as follow: 1) After BSO treatment of 1 mM and 2 mM for 2 days, the intracellular thiol concentration was depleted to 75.7% and 76.2% in SNU-1, and 74.1% and 63.0% in OVCAR-3, respectively. 2) The intracellular thiol concentration in SNU-1 was depleted to 33.4% after BSO 2 mM for only 2 hours incubation and 71.5% after small amount of BSO (0.02 mM) for 2 days. 3) The recovery of intracellular thiol concentration required more than 3 days after BSO removal. 4) BSO inhibited partially the growth of SNU-1 and OVCAR-3. 5) The cytotoxicities of cisplatin and carboplatin were markedly enhanced both in SNU-1 and OVCAR-3 by BSO treatment. 6) The cytotoxicities of radiation was increased in OVCAR-3 and SNU-1 by BSO treatment. Therefore, it is concluded that BSO can deplete effectively the intracellular thiol concentration and enhance the cytotoxicities of cisplatin, carboplatin and radiation.
Figures
References
-
- Gupta V, Singh SV, Ahmand H, Medh RD, Awasthi YC. Glutathione and glutathione S-transferases in a human plasma cell line resistant to melphalan. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989;38:1993. - PubMed
-
- Griffith OW, Meister A. Potent and specific inhibition of glutathione synthesis by buthionine sulfoximine (S-n-butyihomocysteine sulfoximine) J Biol Chem. 1979;254:7558. - PubMed
-
- Green JA, Vistica DT, Young RC, Hamilton TC, Rogan Am, Ozols RF. Potentiation of melphalan cytotoxicity in human ovarian cancer cell lines by glutathione. Cancer Res. 1984;44:5427. - PubMed
-
- Griffith OW. Mechanism of action, metabolism and toxicity of buthionine sulfoximine and its higher homologs, potent inhibitors of glutathione synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1982;257:13704. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
