The effect of dilution, pH and ionic strength of plasma on t-PA precipitation in euglobulin fraction
- PMID: 1306075
- PMCID: PMC4532111
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.1992.7.2.73
The effect of dilution, pH and ionic strength of plasma on t-PA precipitation in euglobulin fraction
Abstract
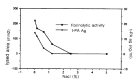
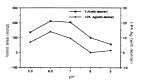
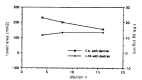
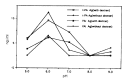
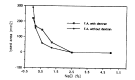
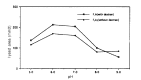
In order to evaluate the influence of dilution, pH and ionic strength on the precipitation of t-PA and PAI-1 during euglobulin precipitation, we measured t-PA Ag, PAI-1 Ag and fibrinolytic activity in the euglobulin fraction made of pooled plasma from liver cirrhosis patients, under various conditions by changing pH, ionic strength and degree of dilution. The precipitation of t-PA Ag in the euglobulin fraction was enhanced by decreasing the ionic strength and greatest at pH 6.0. The fibrinolytic activity in the euglobulin fraction showed consistent changes with t-PA Ag under varying pH and ionic strength. The precipitation of t-PA Ag was not influenced by the dilution factor but the larger the dilution factor, the greater the PAI-1 and the smaller the fibrinolytic activity in the euglobulin fraction. PAI Ag in euglobulin fraction showed consistent changes with t-PA Ag in the euglobulin fraction regardless of the changes in ionic strength and pH. The amount of precipitation of t-PA and PAI-1 was increased by the presence of dextran sulfate, under varying pH, ionic strength and dilution conditions. Our results show that the currently used conditions for standard euglobulin precipitation are the most favorable for t-PA precipitation into the euglobulin fraction. The fibrinolytic activity exerted in the euglobulin fraction seems to depend on the amount of t-PA-PAI-1 complex rather than minimized protease inhibitor in the euglobulin fraction.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Plasminogen activators (t-PA and u-PA) and other fibrinolysis parameters in patients with atherosclerosis obliterans and diabetic macroangiopathy].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2001 Nov;11(65):414-7. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2001. PMID: 11852811 Polish.
-
Amounts of tPA and PAI-1 in the euglobulin fraction obtained at different pH: their relation to the euglobulin clot lysis time.Thromb Res. 1997 Oct 1;88(1):75-80. doi: 10.1016/s0049-3848(97)00193-x. Thromb Res. 1997. PMID: 9336876 No abstract available.
-
PAI-1 plays an important role in the expression of t-PA activity in the euglobulin clot lysis by controlling the concentration of free t-PA.Thromb Haemost. 1991 Oct 1;66(4):474-8. Thromb Haemost. 1991. PMID: 1796399
-
Fibrinolysis during normal human pregnancy: complex inter-relationships between plasma levels of tissue plasminogen activator and inhibitors and the euglobulin clot lysis time.Br J Haematol. 1988 Jun;69(2):253-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1988.tb07630.x. Br J Haematol. 1988. PMID: 3134043
-
Genetic architecture of tissue-type plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1.Semin Thromb Hemost. 2008 Sep;34(6):562-8. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1103367. Epub 2008 Nov 28. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2008. PMID: 19085655 Review.
Cited by
-
Development and application of global assays of hyper- and hypofibrinolysis.Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2019 Nov 6;4(1):46-53. doi: 10.1002/rth2.12275. eCollection 2020 Jan. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2019. PMID: 31989084 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Astrup T, Rasmussen J. Estimation of fibrinologytic activity in blood. Proc. 7 th Int. Congr. Int Soc Haement Rome. 1958:164.
-
- Brakman P, Albrechtsen OK, Astrup T. A comparative study of coagulation and fibrinolysis in blood from normal men and woman. Br J Haematol. 1966;12:74. - PubMed
-
- Kluft C. Elimination of inhibition in euglobulin fibrinolysis by use of flufenamate: Involvement of C1-inactivator. Haemostasis. 1977;6:351. - PubMed
-
- Stead N, Kaplan AP, Rosenberg RD. Inhibition of activiated factor XII by antithrombin-heparin cofactor. J Biol Chem. 1976;251:6481. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
