Small airway disease in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 1306077
- PMCID: PMC4532112
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.1992.7.2.87
Small airway disease in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
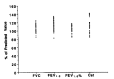
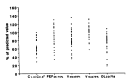
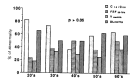
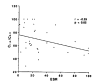
Variety of pulmonary lesions are thought to be associated with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). These lesions traditionally have included pleurisy with or without effusion, Caplan's syndrome, pulmonary rheumatoid nodules, diffuse interstitial fibrosis, and pulmonary arteritis and hypertension. But little attention has been paid to the airways in RA. Recently, several reports have suggested an association between airflow limitation and RA, but its incidence is not known. Also whether there exists a parameter of disease activity of RA, suggesting the presence of small airway disease (SAD) is not clear. To answer these questions, the serologic parameters which reflect the disease activity of RA and pulmonary function tests which reflect small airway dysfunction were performed on 36 lifetime nonsmokers with RA who had normal chest x-ray findings. The prevalence of SAD and the relationships between the disease activity parameters of RA and pulmonary function were observed. The results were as follows. The percentages of patients with abnormal values for diffusing capacity, frequency dependence of compliance (C1.0/C0.0), forced expiratory flow 25-75%, Vmax50% and Vmax 75% were 45.5%, 62.5%, 40%, 22.8% and 11.4%, respectively. There was statistically significant negative correlation between C1.0/C0.0 and ESR. But consistent correlation between other pulmonary function tests and clinical and serologic parameters of RA, and differences in pulmonary function between patients who were serologically positive and negative for CRP and FANA, were not found. In conclusion, SAD, without the influence of smoking, is frequently associated with RA, but the presence of SAD cannot be predicted from any clinical and serologic parameters of RA currently in use.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Visual Assessment of Chest Computed Tomography Findings in Anti-cyclic Citrullinated Peptide Antibody Positive Rheumatoid Arthritis: Is it Associated with Airway Abnormalities?Lung. 2016 Feb;194(1):97-105. doi: 10.1007/s00408-015-9828-1. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Lung. 2016. PMID: 26608346
-
Small airways function in nonsmokers with rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Nov;27(11):1218-26. doi: 10.1002/art.1780271103. Arthritis Rheum. 1984. PMID: 6497918
-
Airways obstruction in rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 1979 Jun;38(3):222-5. doi: 10.1136/ard.38.3.222. Ann Rheum Dis. 1979. PMID: 485577 Free PMC article.
-
Small airway disease and its predictors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Respir Investig. 2022 May;60(3):379-384. doi: 10.1016/j.resinv.2021.12.001. Epub 2022 Jan 3. Respir Investig. 2022. PMID: 34992007
-
Respiratory mechanics measured by forced oscillation technique in rheumatoid arthritis-related pulmonary abnormalities: frequency-dependence, heterogeneity and effects of smoking.Springerplus. 2016 Mar 15;5:335. doi: 10.1186/s40064-016-1952-8. eCollection 2016. Springerplus. 2016. PMID: 27064652 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Bronchiolar disorders in systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases.Eur Respir Rev. 2025 Apr 16;34(176):240248. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0248-2024. Print 2025 Apr. Eur Respir Rev. 2025. PMID: 40240060 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Carr DT, Power MH. Pleural fluid glucose with special reference to its concentration in rheumatoid pleurisy with effusion. Dis Chest. 1960;37:321. - PubMed
-
- Noonan CD, Taylor FB, Engleman EP. Nodular rheumatoid disease of the lung with cavitation. Arthritis Rheum. 1963;6:232. - PubMed
-
- Stack BR, Grant IWB. Rheumatoid interstitial lung disease. Br J Dis Chest. 1965;59:202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
