Coronavirus 229E-related pneumonia in immunocompromised patients
- PMID: 13130404
- PMCID: PMC7107892
- DOI: 10.1086/377612
Coronavirus 229E-related pneumonia in immunocompromised patients
Abstract
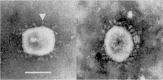
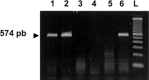
Coronaviruses strains 229E and OC43 have been associated with various respiratory illnesses ranging from the self-resolving common cold to severe pneumonia. Although chronic underlying conditions are major determinants of severe respiratory virus infections, few data about coronavirus-related pneumonia in immunocompromised patients are available. Here we report 2 well-documented cases of pneumonia related to coronavirus 229E, each with a different clinical presentation. Diagnosis was made on the basis of viral culture and electron microscopy findings that exhibited typical crown-like particles and through amplification of the viral genome by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. On the basis of this report, coronaviruses should be considered as potential causative microorganisms of pneumonia in immunocompromised patients.
Figures
References
-
- Soubani AO, Miller KB, Hassoun PM. Pulmonary complications of bone marrow transplantatio. Chest. 1996;109:1066–77. - PubMed
-
- Hendley JO, Fishburne HB, Gwaltney JM., Jr Coronavirus infections in working adults. Eight-year study with 229 E and OC 4. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1972;105:805–11. - PubMed
-
- Wenzel RP, Hendley JO, Davies JA, Gwaltney JM., Jr Coronavirus infections in military recruits. Three-year study with coronavirus strains OC43 and 229. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974;109:621–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

