An inhibitory role for brain serotonin-containing systems in the locomotor effects of d-amphetamine
- PMID: 132524
- PMCID: PMC2913905
An inhibitory role for brain serotonin-containing systems in the locomotor effects of d-amphetamine
Abstract
Locomotor activity induced by d-amphetamine was found to be potentiated by food deprivation, a tryptophan-free diet, p-chlorophenylalanine and drugs proposed to antagonize serotonin receptors in brain. Administration of L-tryptophan 1 hour prior to d-amphetamine injection was found to antagonize the enhanced response to d-amphetamine in starved rats and in rats which had tryptophan removed from their diet. However, tryptophan did not block the potentiated response to d-amphetamine in animals pretreated with p-chlorophenylalanine. These findings suggested that the antagonism of d-amphetamine-induced activity by tryptophan in starved rats and rats fed a tryptophan-free diet was not due to a nonspecific depressant effect of the amino acid. Since accumulation of d-amphetamine and its metabolites was not affected by any of the treatments which enhanced its activity, it seems unlikely that an alteration in the metabolism of d-amphetamine can explain these findings. The present work provides additional support for the view that serotonergic fibers play an important role in the actions of d-amphetamine.
Figures
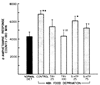
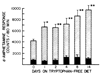
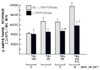
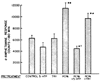
Similar articles
-
Evidence for involvement of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the actions of amphetamine.Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Oct;52(2):307-314. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb09714.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1974. PMID: 4155993 Free PMC article.
-
Differential activity of enantiomers of amphetamine in rats.Neuropharmacology. 1982 Dec;21(12):1323-7. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(82)90141-1. Neuropharmacology. 1982. PMID: 6218425
-
Drug interactions with brain biogenic amines and the effects of amphetamine isomers on locomotor activity.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1978 Apr;8(4):429-35. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(78)90081-3. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1978. PMID: 149988
-
The role of brain 5-hydroxytryptamine in the hyperactivity produced in rats by lithium and monoamine oxidase inhibition.Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Sep;52(1):19-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb09682.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1974. PMID: 4281339 Free PMC article.
-
Motor effects of serotonin in the central nervous system.Life Sci. 1980 Oct 20;27(16):1435-51. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90368-9. Life Sci. 1980. PMID: 6160367 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Interaction of dietary tryptophan and social isolation on territorial aggression, motor activity, and neurochemistry in mice.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1985;87(3):313-21. doi: 10.1007/BF00432714. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1985. PMID: 3936087
-
Lisuride and LSD: dopaminergic and serotonergic interactions in the "serotonin syndrome".Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1979 Nov;65(3):233-7. doi: 10.1007/BF00492209. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1979. PMID: 117494 No abstract available.
-
Behavioral differences between neonatal and adult 6-hydroxydopamine-treated rats to dopamine agonists: relevance to neurological symptoms in clinical syndromes with reduced brain dopamine.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Nov;231(2):343-54. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984. PMID: 6149306 Free PMC article.
-
Neurodegenerative diseases: model organisms, pathology and autophagy.J Genet. 2018 Jul;97(3):679-701. J Genet. 2018. PMID: 30027903 Review.
-
The comparative roles of dopaminergic and serotonergic mechanisms in mediating quipazine induced locomotor activity.J Neural Transm. 1982;54(3-4):145-51. doi: 10.1007/BF01254924. J Neural Transm. 1982. PMID: 7130970 No abstract available.
References
-
- Anton AH, Sayre DF. A study of the factors affecting the aluminium oxide-trihydroxyindole procedure for the analysis of catecholamines. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1962;138:360–375. - PubMed
-
- Anton AH, Sayre DF. The distribution of dopamine and dopa in various animals and a method for their determination in diverse biological material. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1964;145:326–336. - PubMed
-
- Biggio G, Fadda F, Fanni P, Tagliamonte A, Gessa GL. Rapid depletion of serum tryptophan, brain tryptophan, serotonin and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid by a tryptophan-free diet. Life Sci. 1974;14:1321–1329. - PubMed
-
- Bogdanski DF, Pletscher A, Brodie BB, Udenfriend S. Identification and assay of serotonin in brain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1956;117:82–88. - PubMed
-
- Brase DA, Loh HH. Possible role of 5-hydroxytryptamine in minimal brain dysfunction. Life Sci. 1975;16:1005–1016. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
