Morphology of the inner structure of the hippocampal formation in Alzheimer disease
- PMID: 13679273
- PMCID: PMC7973980
Morphology of the inner structure of the hippocampal formation in Alzheimer disease
Abstract
Background and purpose: To our knowledge, inner structural alterations of the hippocampus have never been demonstrated because of the lack of contrast between the hippocampus proper and the superficial medullary lamina. We sought to demonstrate the anatomic details of the inner hippocampus and to elucidate its alterations in Alzheimer disease (AD) in vivo.
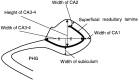
Methods: We obtained multishot diffusion- and T2-weighted MR images in 14 healthy control subjects and 26 patients with mild or moderate AD (diagnosis based on Mini-Mental Status Examination scores). We measured the width of the subiculum, CA1 and CA3-4, and the height of CA3-4 on coronal images.
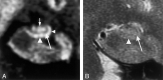
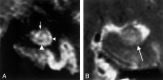
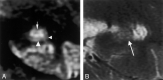
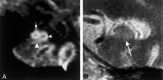
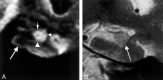
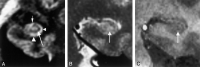
Results: The subiculum and hippocampus proper were demonstrated as whirlpool-shaped hyperintense areas, and the superficial medullary lamina was visible as a hypointense structure along the inner margin of the hippocampus proper. Regarding the width of the subiculum and CA1, intergroup analysis revealed significant differences between the control and mild or moderate AD groups. In the width of CA3-4, we found no significant difference between the control and mild AD groups; however, differences between the control and moderate AD groups and between the mild and moderate AD groups were significant. In the height of CA3-4, we observed no significant differences between groups.
Conclusion: We clearly visualized the inner structure of the hippocampal formation by using multishot diffusion-weighted imaging. The subiculum and CA1 are the most vulnerable regions in AD, and atrophy of these structures was evident in both mild and moderate AD.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hippocampal shape analysis in Alzheimer's disease: a population-based study.Neuroimage. 2007 May 15;36(1):8-18. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.12.036. Epub 2007 Mar 12. Neuroimage. 2007. PMID: 17434756
-
In vivo detection of microstructural correlates of brain pathology in preclinical and early Alzheimer Disease with magnetic resonance imaging.Neuroimage. 2017 Mar 1;148:296-304. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.12.026. Epub 2016 Dec 15. Neuroimage. 2017. PMID: 27989773 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo neuropathology of the hippocampal formation in AD: a radial mapping MR-based study.Neuroimage. 2006 Aug 1;32(1):104-10. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.03.015. Epub 2006 May 2. Neuroimage. 2006. PMID: 16631382
-
Diffusion-weighted MR of the brain: methodology and clinical application.Radiol Med. 2005 Mar;109(3):155-97. Radiol Med. 2005. PMID: 15775887 Review. English, Italian.
-
Challenges of High-resolution Diffusion Imaging of the Human Medial Temporal Lobe in Alzheimer Disease.Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2010 Dec;21(6):355-65. doi: 10.1097/RMR.0b013e31823f6413. Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2010. PMID: 22158129 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of ivabradine on cognitive functions of rats with scopolamine-induced dementia.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 10;12(1):16970. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-20963-5. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36216854 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between volume and morphological changes in the hippocampal formation in Alzheimer's disease: rounding of the outline of the hippocampal body on coronal MR images.Neuroradiology. 2012 Oct;54(10):1079-87. doi: 10.1007/s00234-012-1019-7. Epub 2012 Feb 16. Neuroradiology. 2012. PMID: 22349566
-
Diffusion tensor microscopy indicates the cytoarchitectural basis for diffusion anisotropy in the human hippocampus.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007 May;28(5):958-64. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007. PMID: 17494678 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effects of carnosic Acid in an experimental model of Alzheimer's disease in rats.Cell J. 2011 Spring;13(1):39-44. Epub 2011 Apr 21. Cell J. 2011. PMID: 23671826 Free PMC article.
-
mNos2 deletion and human NOS2 replacement in Alzheimer disease models.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2014 Aug;73(8):752-69. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0000000000000094. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2014. PMID: 25003233 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mohs RC, Doody RS, Morris JC, et al. A 1-year, placebo-controlled preservation of function survival study of donepezil in AD patients. Neurology 2001;57:481–488 - PubMed
-
- Winblad B, Engedal K, Soininen H, et al. A 1-year, randomized, placebo-controlled study of donepezil in patients with mild to moderate AD. Neurology 2001;57:489–495 - PubMed
-
- Doody RS, Geldmacher DS, Gordon B, Perdomo CA, Pratt RD. Open-label, multicenter, phase 3 extension study of the safety and efficacy of doneprzil in patients with Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 2001;58:427–433 - PubMed
-
- Dickerson BC, Goncharova I, Sullivan MP, et al. MRI-derived entorhinal and hippocampal atrophy in incipient and very mild Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 2001;22:747–754 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
