Pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration: MR imaging, proton MR spectroscopy, and diffusion MR imaging findings
- PMID: 13679293
- PMCID: PMC7973979
Pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration: MR imaging, proton MR spectroscopy, and diffusion MR imaging findings
Abstract
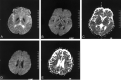
We herein report the case of a 15-year-old male patient with pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration. The classic "eye-of-the-tiger" appearance was initially present on the globus pallidi on T2-weighted MR images and had disappeared by the time of the 10-month follow-up examination. Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery images revealed marked hypointensity in the globus pallidi and dentate nuclei and high signal intensity changes in the deep cerebral white matter. Proton MR spectroscopy revealed markedly decreased N-acetylaspartate in the globus pallidi, associated with decreased N-acetylaspartate and increased myoinositol in the deep cerebral white matter. Diffusion MR images (b=1000 s/mm(2)) were negative (normal appearing) for deep cerebral white matter lesions, whereas apparent diffusion coefficient values were slightly increased (1.08-1.12 x 10(-3) mm(2)/s), compared with the apparent diffusion coefficient values from the normal white matter regions. Apparent diffusion coefficient values in the globus pallidi were lower than those in the unaffected thalamus.
Figures


References
-
- Singhi PD, Mitra S. Hallervorden-Spatz disease: late infantile type. J Child Neurol 1997;12:281–282 - PubMed
-
- Hickman SJ, Ward NS, Surtees RA, Stevens JM, Farmer SF. How broad is the phenotype of Hallervorden-Spatz disease? Acta Neurol Scand 2001;103:201–203 - PubMed
-
- Tiamkao S, Nitinavakarn B, Jitpimolmard S. Hallervorden-Spatz syndrome in two siblings diagnosed by clinical features and magnetic resonance imaging. J Med Assoc Thai 2000;83:1535–1540 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
