Biochemical properties of chimeric skeletal and smooth muscle myosin light chain kinases
- PMID: 1371510
- PMCID: PMC2836765
Biochemical properties of chimeric skeletal and smooth muscle myosin light chain kinases
Abstract
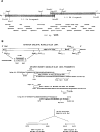
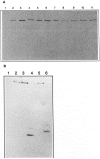
The molecular and biochemical properties of myosin light chain kinases from chicken skeletal and smooth muscle were investigated by recombinant DNA techniques. Deletion of the amino-terminal region of either the smooth or skeletal muscle myosin light chain kinase resulted in a decrease in Vmax with no significant change in Km values for light chain substrates. Skeletal/smooth muscle chimeric kinases were inactive when a 65-residue region amino-terminal of the catalytic core was exchanged between the two forms. Changing alanine 494 to glutamic acid within this region in the chicken skeletal muscle myosin light chain kinase increased the Km values for light chains 10-fold. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that the region amino-terminal of the catalytic core in myosin light chain kinases is involved in light chain recognition. A skeletal muscle kinase which contained the smooth muscle calmodulin binding domain remained regulated by Ca2+/calmodulin. Thus, the calmodulin binding domains of smooth and skeletal muscle myosin light chain kinases share structural elements necessary for regulation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Regulatory segments of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases.J Biol Chem. 1998 Apr 10;273(15):8951-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.15.8951. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9535879
-
Substrate specificity of myosin light chain kinases.J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25945-50. J Biol Chem. 1992. PMID: 1464607
-
The calmodulin binding domain of chicken smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase contains a pseudosubstrate sequence.J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2542-8. J Biol Chem. 1987. PMID: 3818608
-
Structure and function of a calmodulin-dependent smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase.Experientia. 1984 Nov 15;40(11):1185-8. doi: 10.1007/BF01946645. Experientia. 1984. PMID: 6094232 Review.
-
Myosin light chain kinase: functional domains and structural motifs.Acta Physiol Scand. 1998 Dec;164(4):471-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-201x.1998.tb10699.x. Acta Physiol Scand. 1998. PMID: 9887970 Review.
Cited by
-
Myosin light chain kinase from skeletal muscle regulates an ATP-dependent interaction between actin and myosin by binding to actin.Mol Cell Biochem. 1999 Jan;190(1-2):85-90. Mol Cell Biochem. 1999. PMID: 10098974
-
Myosin light chain kinases.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1997 Feb;18(1):1-16. doi: 10.1023/a:1018616814417. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1997. PMID: 9147985 Review. No abstract available.
-
A molecular mechanism for autoinhibition of myosin light chain kinases.J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26578-82. J Biol Chem. 1993. PMID: 8253787 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin phosphatase and myosin phosphorylation in differentiating C2C12 cells.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2003;24(8):499-511. doi: 10.1023/b:jure.0000009810.36038.53. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2003. PMID: 14870965
-
Localization of an actin binding domain in smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase.Mol Cell Biochem. 1997 Aug;173(1-2):51-7. doi: 10.1023/a:1006876318155. Mol Cell Biochem. 1997. PMID: 9278254
References
-
- Adelstein RS, Klee CB. J. Biol. Chem. 1981;256:7501–7509. - PubMed
-
- Andersson S, Davis DL, Dahlbäch H, Jörnvall H, Russell DW. J. Biol. Chem. 1989;264:8222–8229. - PubMed
-
- Bagchi IC, Kemp BE, Means AR. J. Biol. Chem. 1989;264:15843–15849. - PubMed
-
- Blumenthal DK, Stull JT. Biochemistry. 1982;21:2386–2391. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

