FK 506 and autoimmune disease: perspective and prospects
- PMID: 1382646
- PMCID: PMC2967358
- DOI: 10.3109/08916939209148473
FK 506 and autoimmune disease: perspective and prospects
Figures
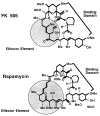
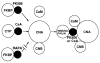
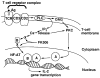
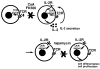
Similar articles
-
Summary of the First International FK 506 Congress: perspectives and prospects.Transplant Proc. 1991 Dec;23(6):3371-5. Transplant Proc. 1991. PMID: 1721464 No abstract available.
-
[Clinical experience with FK 506].Presse Med. 1991 Nov 27;20(40):1967-73. Presse Med. 1991. PMID: 1722311 Review. French.
-
FK-506--a novel immunosuppressant.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Jun 23;685:22-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb35847.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993. PMID: 7689805 Review. No abstract available.
-
FK 506: a novel immunosuppressant for treatment of autoimmune disease. Rationale and preliminary clinical experience at the University of Pittsburgh.Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1993;14(4):323-44. doi: 10.1007/BF00192307. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1993. PMID: 7686690 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
[Treatment with tacrolimus in autoimmune diseases].Rev Med Univ Navarra. 2004 Jul-Sep;48(3):24-38. Rev Med Univ Navarra. 2004. PMID: 15622922 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Immunophilins, Refsum disease, and lupus nephritis: the peroxisomal enzyme phytanoyl-COA alpha-hydroxylase is a new FKBP-associated protein.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Mar 2;96(5):2104-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.5.2104. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10051602 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes tolerogenic vaccines targeting antigen-specific inflammation.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015;11(2):522-30. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2014.1004024. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015. PMID: 25622092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suppression of autoimmune thyroid disease by FK 506: influence on thyroid-infiltrating cells, adhesion molecule expression and anti-thyroglobulin antibody production.Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Mar;91(3):368-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb05911.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993. PMID: 7680293 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of combined administration of FK 506 and the purine biosynthesis inhibitors mizoribine or mycophenolic acid on lymphocyte DNA synthesis and T cell activation molecule expression in human mixed lymphocyte cultures.Transpl Immunol. 1993;1(2):146-50. doi: 10.1016/0966-3274(93)90009-w. Transpl Immunol. 1993. PMID: 7521738 Free PMC article.
-
New immunosuppressive drugs: mechanistic insights and potential therapeutic advances.Immunol Rev. 1993 Dec;136:71-98. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1993.tb00655.x. Immunol Rev. 1993. PMID: 8132204 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kino T, Hatanaka H, Hashimoto M, Nishiyama M, Goto T, Okuhara M, Kohsaka M, Aoki H, Imanaka H. FK 506, a novel immunosuppressant isolated from Streptomyces. I. Fermentation, isolation and physicochemical and biological characteristics. J Antibiot. 1987;40:1249–1255. - PubMed
-
- Kino T, Hatanaka H, Miyata S, Inamura N, Nishiyama M, Yajima T, Goto T, Okuhara M, Kohsaka M, Aoki H, Ochiai T. FK 506, a novel immunosuppressant isolated from a Streptomyces. II. Immunosuppressive effect of FK 506 in vitro. J Antibiot. 40:1256–1265. - PubMed
-
- Thomson AW. FK 506. How much potential? Immunol Today. 1989;10:6–9. - PubMed
-
- Kahan BD, Chang JY, Seghal SN. Preclinical evaluation of a new potent immunosuppressive agent rapamycin. Transplantation. 1991;52:185–191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
