Synthesis and biological activity of N6-(p-sulfophenyl)alkyl and N6-sulfoalkyl derivatives of adenosine: water-soluble and peripherally selective adenosine agonists
- PMID: 1433217
- PMCID: PMC3420980
- DOI: 10.1021/jm00100a020
Synthesis and biological activity of N6-(p-sulfophenyl)alkyl and N6-sulfoalkyl derivatives of adenosine: water-soluble and peripherally selective adenosine agonists
Erratum in
- J Med Chem 1993 Oct 15;36(21):3218
Abstract
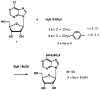
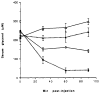
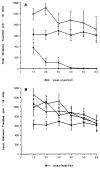
A series of N6-(p-sulfophenyl)alkyl and N6-sulfoalkyl derivatives of adenosine was synthesized, revealing that N6-(p-sulfophenyl)adenosine (10b) is a moderately potent (Ki vs [3H]PIA in rat cortical membranes was 74nM) and A1-selective (120-fold) adenosine agonist, of exceptional aqueous solubility of > 1.5 g/mL (approximately 3 M). Compound 10b was very potent in inhibiting synaptic potentials in gerbil hippocampal slices with an IC50 of 63 nM. At a dose of 0.1 mg/kg ip in rats, 10b inhibited lipolysis (a peripheral A1 effect) by 85% after 1 h. This in vivo effect was reversed using the peripherally selective A1-antagonist 1,3-dipropyl-8-[p-(carboxyethynyl)phenyl]xanthine (BW1433). The same dose of 10b in NIH Swiss mice (ip) was nearly inactive in locomotor depression, an effect that has been shown to be centrally mediated when elicited by lower doses of other potent adenosine agonists, such as N6-cyclohexyladenosine (CHA) (Nikodijevic et al. FEBS Lett. 1990, 261, 67). HPLC studies of biodistribution of a closely related and less potent homologue, N6-[4-(p-sulfophenyl)butyl]adenosine indicated that a 25 mg/kg ip dose in mice resulted in a plasma concentration after 30 min of 0.46 micrograms/mL and no detectable drug in the brain (detection limit < 0.1% of plasma level). Although 10b at doses > 0.1 mg/kg in mice depressed locomotor activity, this depression was unlike the effects of CHA and was reversible by BW1433. These data suggest that 10b is a potent adenosine agonist in vivo and shows poor CNS penetration.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Binding of the radioligand [3H]-SCH 58261, a new non-xanthine A2A adenosine receptor antagonist, to rat striatal membranes.Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Apr;117(7):1381-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15296.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8730729 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine receptor prodrugs: synthesis and biological activity of derivatives of potent, A1-selective agonists.J Pharm Sci. 1994 Jan;83(1):46-53. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600830112. J Pharm Sci. 1994. PMID: 8138909 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of A1 and A2 adenosine receptors in the rat spinal cord.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Sep;242(3):905-10. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987. PMID: 3656118
-
Inhibition of N6-[3H]cyclohexyladenosine binding by carbamazepine.Epilepsia. 1990 Sep-Oct;31(5):503-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1990.tb06098.x. Epilepsia. 1990. PMID: 2401242
-
7-Deaza-2-phenyladenines: structure-activity relationships of potent A1 selective adenosine receptor antagonists.J Med Chem. 1990 Oct;33(10):2822-8. doi: 10.1021/jm00172a023. J Med Chem. 1990. PMID: 2213835
Cited by
-
Adenosine A₁ receptors in mouse pontine reticular formation modulate nociception only in the presence of systemic leptin.Neuroscience. 2014 Sep 5;275:531-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.06.025. Epub 2014 Jun 26. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24976513 Free PMC article.
-
Contractile effects of adenosine, coronary flow and perfusion pressure in murine myocardium.Pflugers Arch. 2007 Jan;453(4):433-41. doi: 10.1007/s00424-006-0119-9. Epub 2006 Oct 28. Pflugers Arch. 2007. PMID: 17072640
-
A binding site model and structure-activity relationships for the rat A3 adenosine receptor.Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Jun;45(6):1101-11. Mol Pharmacol. 1994. PMID: 8022403 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of A3 adenosine receptor agonists as novel non-narcotic analgesics.Br J Pharmacol. 2016 Apr;173(8):1253-67. doi: 10.1111/bph.13446. Epub 2016 Mar 6. Br J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26804983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions of flavonoids and other phytochemicals with adenosine receptors.J Med Chem. 1996 Feb 2;39(3):781-8. doi: 10.1021/jm950661k. J Med Chem. 1996. PMID: 8576921 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Durcan MJ, Morgan PF. NECA-induced hypomotility in mice: Evidence for a predominantly central site of action. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1989;32:487–490. - PubMed
-
- Barraco RA, Bryant SD. Depression of locomotor activity following bilateral injections of adenosine analogs into the striatum of mice. Med Sci Res. 1987;15:421–422.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
